Integrated Logistics is a goal to achieve customer’s satisfaction at the lowest total cost with a one-stop solution to the shipping and logistic requirements of the company. Integrated Logistics refers to specific logistics practices and operational activities that coordinate the flow of materials from suppliers to the customers throughout the value stream.
A strong integrated logistics system needs a clear frame of logistics and a proper transport implements and techniques to link the producing procedures. The elements of a successful Integrated Logistics practice include low stock levels, just in time delivery and the possibility of goods replacement depending on timely and accurate flow of information.
Table of Contents
What is Transportation?
Transportation is a component of international logistics network, managing and controlling the flow of goods, energy, information and other resources like products, services, and people, from the source of products to marketplace. The operation of transportation determines the efficiency of moving products from point A to point B involving long distance movement.
The progress in techniques and management principles improves the moving load, delivery speed, service quality, operation costs, the usage of facilities and energy saving. Transportation takes a crucial part in the manipulation of logistic.

Warehousing
Warehousing is part of a logistics management system, and is a key component for effective management of supply chain. The purpose of warehousing is to store materials and finished goods. The inbound functions prepare items for storage, whereas the outbound functions consolidate, pack and ship orders. The objective goal of warehousing is to integrate with transportation and ensure on-time delivery of goods. Inbound logistics refers to the transport, storage and delivery of goods, as well as transportation requirements, to facilitate either manufacturing or market distribution. Outbound logistics refers to warehousing, packaging and transporting of goods, moving the final product and related information flows from the end of the production line to the end consumer.
Proper Planning
An efficient proper planning of transportation can help companies to reduce various risks such as the cost of overpay, missed delivery targets, damaged of goods, and lose of valuable business. The purpose of proper planning of transportation can enhance efficiency, and achieve significant cost reduction. Reduced costs in transportation lead to savings that trickle down to the bottom line.
That is because transportation typically involves bringing production supplies, components, and finished goods into the company or delivering goods to customers, so whenever money can be saved, it goes right to profit.
Mode of Transportation
The selection of mode of transportation will be the dictating factor of success for transporting goods in business logistics. Transportation modes are essential components of transport systems since they are the means by which mobility is supported. These are important factors to be considered while selecting the available modes of transportation are such as type of products, cost, speed, reliability and capability. The operating characteristics of different transportation modes are shown as below table.
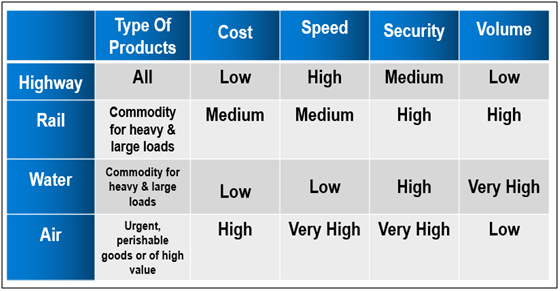
Type of Products
The type of products is the most important factor to be considered while choosing a mode of transportation in a business logistics. The product can be Perishable items like food products, Non-Perishable item like machine components or Dangerous products like Inflammable goods, etc. Only after gaining knowledge of this factor, other can be determined and planned for transportation.
The transportable goods can be finished products, raw materials or semi-finished goods for processing at different locations. The flow of transporting goods in a business logistics are simply divided as
• Inbound logistics is the process flow of raw materials shipped to your business for manufacturing purposed.
• Internal logistics is the movement of raw materials and finished goods from one department of your business to another.
• Outbound logistics refers to the preparation for shipment, and the transportation, of the finished products to marketplace or end customer.
By categorizing the products in such, most problems can be easily identified and bottlenecks can be avoided, which ease the process of planning and prioritizing the goods for transportation.

Speed and Availability of Service
The speed of the service, or time elapsed in moving products from one facility to another, and finally to the customer, is often more important than the cost of service. Slower mode of transportation involves lower transportation cost, which also result in lower service levels. The availability depends on the existing transportation.
Weight and Volume of Shipment
Weight and volume of a shipment need to be calculated during the planning phase of transporting goods. The weight and volume determine the optimal mode of transportation after considering the above-mentioned factors as well.
The cost of transporting a shipment can be affected by the amount of weight and volume. A product with lower weight but a higher volume will require more or bigger vehicles for transport. Whereas, products with a lower volume but a higher weight will require the use of stronger vehicles for transport.
Urgent, perishable goods or high-value products can use air frights for transportation. Large volume exports need to be cost-efficient, thus water transportation is the right mode of transportation.

Security of Goods
The quality and security of the transporting goods also need to be factored in for establishing a successful supply chain. In business logistics, the products must be transported with minimum loss and damage during transportation. Insuring your products for shipping of the goods protects you from accidental damage to loss of goods due to misplacement.
Packaging also plays a vital role in the transporting of goods. Some products require waterproof packing and some for easy transportation. Depending on the requirements, the goods have to be packed securely for the transportation.
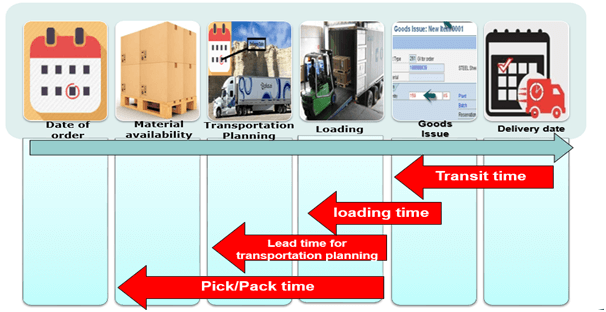
Transit Time of Transportation
Time is one of the crucial factor in transportation and logistics management. Products have to reach on agreed time for a smoother operation during transportation. Calculations for time required to source the product, load, unload, emergency and breakdowns need to be added in planning of transportation for shipment.
A delay during transport of perishable goods has the risk of losing the entire shipment. If the product is not delivered upon agreed date and time, the customer might cancel the business order due to the change in demand for sales or manufacturing. Thus, time needs to be factored in while transporting goods.
Seven “RIGHTS” of Transportation for Integrated Logistics
As logistics managers sought to make the value-added contribution of logistics more visible to upper management, the “seven rights” of transportation were coined and publicized. The seven rights are, to deliver the right product, in the right quantity and the right condition, to the right place at the right time for the right customer at the right price. These seven rights highlight the importance of moving and storing materials in an efficient, timely, and reliable manner. The seven rights also link logistics to the key strategic objectives of cost competitiveness, quality, flexibility, and delivery. The seven rights demonstrate logistic activities which provide the foundation for high levels of customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Transportation play a crucial part and influences the performance in the manipulation of integrated logistic. The operation of transportation determines the efficiency of delivering products from resource into practical goods and it will contribute to reduce operation cost. Therefore, the above-mentioned are the key transport considerations leading to a competitive strategy for a firm.
References
Abi Teh Ching Yee, DLSM. (2018). “Essential Strategies for Managing Freight Forwarding”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/essential-strategies-managing-freight-forwarding/, accessed 18/12/2019.
Dheerthan Gajapathy. (2017) “8 Factors to Consider When Transporting Goods in Business Logistics. Retrieved from: https://www.trdinoo.com/2017/transporting-goods-business-logistics/, accessed 16/12/2019.
Leong King Fatt Cyrus, DLSM. (2019). “Integrated Logistics Practices for the Food Industry”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/integrated-logistics-practices-food-industry/, accessed 17/12/2019.
LTD Management. (2019) “Transport Strategy” Retrieved from https://www.ltdmgmt.com/transportation-strategy.php, accessed 16/12/2019.
Max Galarza Hernandez. (2016). “Integrated logistics transportation” Retrieved from: https://www.slideshare.net/maxgalarza/integrated-logistics-transportation, accessed 15/12/2019.
Sonia Lai Jie Yin, DLSM. (2018). “Key Success Factors For Effective Logistics Practices”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/key-success-factors-effective-logistics-practices/, accessed 16/12/2019.

