Technological developments and digital commerce are gradually disrupting procurement, logistics, and supply chain. With rapid technological revolutionize around the world, the organization is facing rapid change in the way the business is being conducted.
Blockchain Technology not just apply to the immediate context of currency and payments (Blockchain 1.0), or to contracts, property, and all financial markets transactions (Blockchain 2.0), but beyond to segments as diverse as government, health, science, literacy, publishing, economic development, art, and culture (Blockchain 3.0), and heterogeneous forest network (Blockchain 4.0). Like any new technology, Blockchain technology is an idea that initially disrupts.
Table of Contents
Key Features of Blockchain Technology
1. A Blockchain record cannot be controlled by a single entity
It needs to take control of more than 51% of all the networked computers controlling the Blockchain to amend the record. If your network is a million strong computers, a seemingly impossible event. From a single computer, a request to add can only be processed, and also to view the current Blockchain record.
2. Information recorded is shared by a large number of entities
If one computer is corrupted for some reason and is offline, the other computers in the Blockchain network will still maintain the Blockchain record. Each computer in the Blockchain network will have a copy of the Blockchain record. This ensures that no matter what happens, there is a build in fail-safe in information records, be it man-made or natural equipment failures. This useful feature becomes critical if your supply chain system is connected worldwide, having a decentralized data system like Blockchain technology will make it robust to any centralized system failures, making information recovery swift ensuring continuous supply chain operations and almost impossible to hack.
3. Information recorded in a Blockchain cannot be corrupted
The programmed protocol of a Blockchain record does not allow for modification of entries already added previously. Which bring us to the point that Blockchain technology ensures information integrity which is tamper-proof to a higher degree. This comes useful for supply chain information systems that are reliant on corrupt proof information at all nodes of the supply chain system. Examples of this use would be like pharmaceuticals, where traceability and manufacturing origin is vital to prevent fake products from distribution in a market.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Today we are going to discuss five possible applications in digital supply Chain:
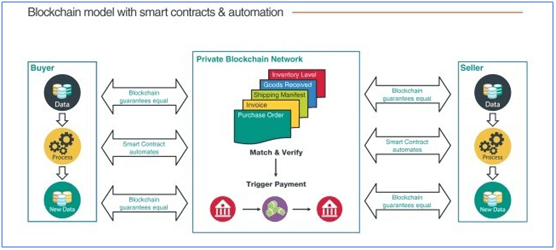
1. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts is used to execute an action when criteria is fulfilled. It is a computer protocol intended to digitally facilitate, verify, or enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract. In additional, it allows the performance of credible transactions without third parties.
An example of a purchase where payment is in stages like a 10% up front and 90% upon receiving item. So the 10% down payment triggers the build of the product in Blockchain records. All the subsequent activities get recorded to the Blockchain. Once the item gets received by the customer an auto release from the bank is initiated for the balance 90% payment. This can only happen only if all the required activities are fulfilled earlier like quality acceptance, safe delivery to customer and finally digitally acceptance received by customer.
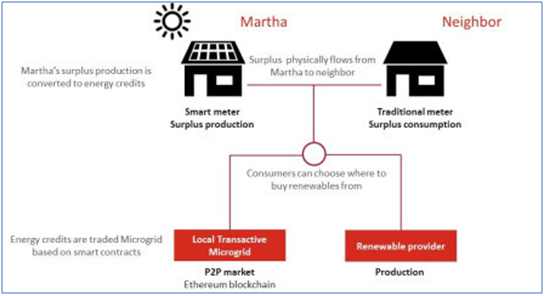
2. Peer-to-Peer Transfer
Blockchain technology allows for secure transfer of data or electronic payment without the use of a central host. With a two key encryption for the sender and receiver, the Blockchain network packs the Blockchain across the internet and the receiver then receives the data or payment without any middleman.
An example of Peer-to-Peer Energy Microgrid. Power Ledger has software which can read the outputs of electricity meters, measure the amount of energy that is consumed or generated. It is a Blockchain based peer-to-peer energy trading platform enabling consumers and businesses to sell their surplus solar power to their neighbors without a middleman. The buyer receives the energy and the seller’s bank make payment for the electricity via smart contracts.
3. Product Trail Recording from Origin to Customer
The ultimate product traceability tool. With Blockchain technology, one can track how the product gets from the supplier to the producer, and how it is distributed. It is possible to get information about the origin and destination of the product. Furthermore, it can be seen how a retailer adds potential information about its usage and provides an additional application for customers. Lastly, the buyer gets full knowledge about the origin of the product, its delivery time, and additional facts about its consumption. This type of recording is ideal for aerospace components, pharmaceuticals, food safety control, medical devices, etc. An example of a Dry aged beef supply chain is shown below.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Adrian Goh, GDSCM. (2017). “Blockchain Technology – The Next Revolution of Supply Chain”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/blockchain-technology-next-revolution-supply-chain, accessed 30/08/2018.
Applicature.com (2018). “How to Apply Blockchain to Supply-Chain Management”. Retrieved from https://medium.com/applicature/how-to-apply-blockchain-to-supply-chain-management-8cc673c66c4c, accessed 30/08/2018.
Pcruikshank, HC. (2017). “Blockchain Peer Peer Energy Microgrid”. Retrieved from https://makeasmartcity.com/2017/10/12/blockchain-peer-peer-energy-microgrid, accessed 30/08/2018.
Pramod, C. (2017). “Blockchain Technology Part 2: Smart Contract Fundamentals”. Retrieved from https://codeburst.io/blockchain-technology-part-2-smart-contract-fundamentals-d243e2311f94, accessed 30/08/2018.
Srinivasan Varadarajulu, ADPSM.(2018). “Blockchain Technology Enabling Seamless Supply Chain”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/blockchain-technology-enabling-seamless-supply-chain, accessed 30/08/2018.

