Warehouse describes a facility where it served the purpose of storing goods. In ecommerce, warehouses are mainly used to keep items on stock to make sure the short delivery times needed can be fulfilled. Obviously, there are many other uses for warehouses outside of ecommerce. Just think of production warehouses with parts or warehouses to serve as a buffer between production and expedition. Whatever the use of a warehouse, they all follow the same principle of inbound-storage-outbound processes: stuff comes in, is stored, and goes out again.

Table of Contents
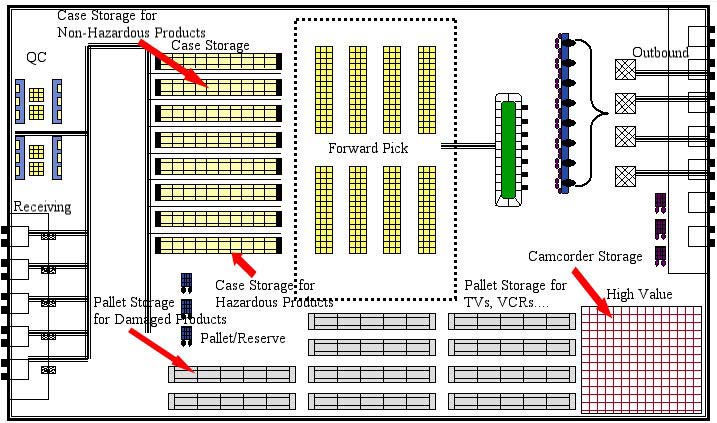
1. Layout of the warehouse
To facilitate a good flow, it is important that internal warehouse layout must be associated with external warehouse layout. Congestion outside the warehouse, caused by parking area constraints can also affect all warehouse activities. So it is very important to manage warehouse layout efficiency both in terms of internal and external space to ensure that potential bottlenecks will not impact warehouse productivity. There are also other factors to look out for the layout of a warehouse.
a) Future storage requirement – Forecasting your stock profiles and access requirements are key factors to consider before any re-planning of your warehouse space can begin.
b) Adaptability – Even careful forecasting won’t account for every subtle shift in requirements throughout the life of your warehouse. In order to best prepare yourself for these changes, keep ease of adaptability in mind when designing the original layout. As your sales volumes increase, or the design or sizing product packaging changes, may find yourself in urgent need of extra space or a different kind of storage. These changes can potentially cost a lot of time, money and resources if a major overhaul is needed. So designing your warehouse layout to easily accommodate small changes can save you a lot of hassle.
c) Flow of warehouse – A major factor drastically affecting warehouse layout is the flow of goods within the facility. If your warehouse is an existing structure, then the decision may already be made for you due to the current positioning of docks and loading bays. If you are building a new facility however, think about which system best suits your needs.
d) Types of racking – Storage and pallet racking comes in many different sizes, shapes and formats, and the type you use will depend heavily on the types of products you are storing. Carefully consider your requirements as this will affect the amount of space you require and influence the layout of the facility as a whole. A common practice now is to effectively build your warehouse from the inside-out; this ensures you will have adequate space for racking and other facilities.
2. Receiving
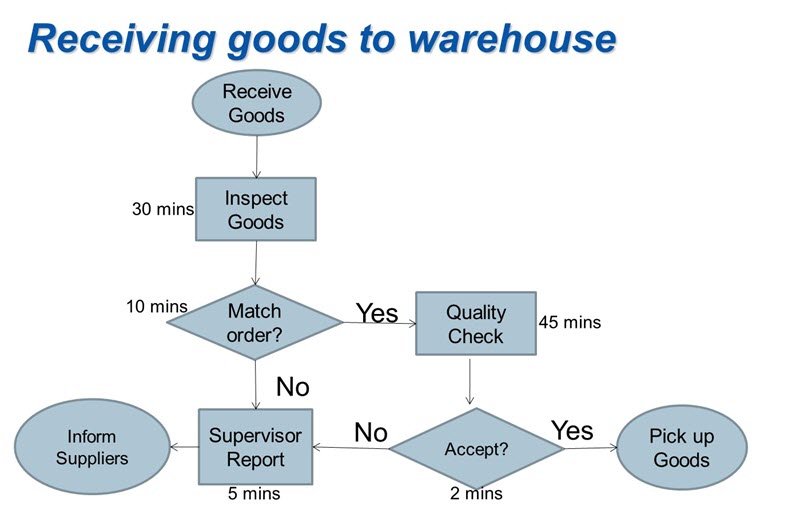
Receiving area are the most active area fill with activity almost all the time. Any potential bottleneck cause in that area, might have a bad impact towards the operation work flow. Applying a standard turn for each transporter to enter the loading dock, may reduce congestion. It might be time consuming, but it gives the advantage for the receiver to clear the receiving area before the next transporter comes in. It can also reduce the chance of mistake during receiving as the checker would not be made to rush while checking all the incoming stocks. The following steps and procedures are performed by Central Receiving staff;
a) Checking all the material/goods received against the supplier’s packing document.
b) Inspect all external packages for any visual damage. If visible damage is apparent, conduct a more thorough inspection of the contents of the packages to look for obvious damage to the item in the carton or container.
c) All completed received goods are immediately fork away to the put away central.
Any products found with damage packaging or variance in quantity, must be indicated on the receiving document. Picture of the damage parts are also required to be taken for record purposes. Report the damage to the proper authority in the organization.
3. Put Away
Put Away refers to the process of keeping any goods in the Final Position of the Warehouse for storing. It is a process from receiving the item at the location of the warehouse and then carrying it to the final position where products of this kind are stored. Locating free locations (put-away) is a key capability of a warehouse management system (WMS). Put-away is normally thought of as the process of moving received inventory from the dock, kitting area, or production department to a storage bin. The put-away process is also used to relocate inventory within the warehouse and to replenish dedicated storage bins with inventory from a reserve storage bin. Any time inventory is being placed in a storage bin it is being put away.
4. Material Handling Equipment
Material handling equipment is mechanical equipment used for the movement, storage, control and protection of materials, goods and products throughout the process of manufacturing, distribution, consumption and disposal. Good materials handling is important because it will help you in many ways.
There are also advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages
a) Reduce damage of goods
b) Reduce injury cause by manual handling
c) Reduce time needed for transferring of goods around
Disadvantages
a) Extra cost needed for maintainace
b) Any mechanism failure means a longer downtime in production
c) Additional cost for purchasing a equipment
d) Skillful personnel to operate any mechanical equipment
5. Picking
Picking or order preparation is one of a logistic warehouse’s process. It consists in taking and collecting articles in a specified quantity before shipment to satisfy customers’ orders. It is a basic warehousing process and has an important influence on supply chain’s productivity. Mixing multiple SKUs in the same bin location reduces picking productivity. Batch and cluster order picking strategies are used in warehouses. Travel time can easily account for 50% or more of order picking hours. By combining orders into a single travel instance the time spent travelling is greatly reduced. Order picking productivity improves if an operator picks from one out of every 100 pick locations will be slower than if the operator picks from one out of every 10 pick locations. Warehouse efficiency will also improve when items are assigned to the correct storage media.
Conclusion
Warehouse plays a crucial rule in integrated supply chain operation and make a positive contribution. The appropriate operations function in a warehouse not only improve customer service, but also bring profit as well. To ensure perfect operation of a warehouse, a good layout planning and work flow should be implement. Purchasing team should also develop delicate program for supplier measurement and establish good relationship with all suppliers to ensure timely and abundant supplement.
References:
Hector Sunol (2017) “Warehouse Operations: Optimizing the Receiving Process
Retrieved from: http://articles.cyzerg.com/warehouse-operations-optimizing-the-receiving-process
Jeff Howard (2017) “7 Tips for an Improved Warehouse Workflow”
Retrieved from: https://www.sjf.com/blog/improved-warehouse-workflow
Janvi (2017) “Why Material Handling Is Important
Retrieved from: http://www.carneyfabricating.com/why-materials-handling-is-important/
Martin Murray (2017) “Planning And Optimizing Your Warehouse Layout-Supply Chain Impact”
Retrieved from: https://www.thebalance.com/planning-your-warehouse-layout-2221065
Marc Wulfaat (2013) “5 Ways to Improve Order Picking Productivity
Retieved from: http://www.supplychain247.com/article/5_ways_to_improve_order_picking_productivity/MWPVL_International

