Global sourcing is the practice of sourcing from the global market for goods and services across geopolitical boundaries. Global sourcing is often designed to deliver products or services using global efficiencies. These efficiencies include low-cost skilled labour, low-cost raw materials and other economic factors such as tax breaks and low trade tariffs. Global sourcing is often associated with a centralized procurement strategy for a multinational, wherein a central buying organization seeks economies of scale through corporate-wide standardization and benchmarking.
Finding a rock-bottom price is not the problem, but landing great costs while avoiding distance, timing, quality, and language problems can be challenging. If you ignore or mishandle these risks, they can result in cost penalties and distracting inefficiencies.
Table of Contents
Preliminary Research
The process will be started by setting the stage for the upcoming procurement project. It requires researcher to be open to innovative solutions without losing sight of the goals, focus on the goals by clarifying the scope and goals of the procurement projects. In the process, a team of purchaser to be set up to pursue the expected results of the procurement project. Companies also need to identify the core and non-core business activities, analyse customer and market needs, and identify competitors. The idea is to develop the firm’s business objectives, prospective markets and brand positioning.
Market and Supplier Evaluation
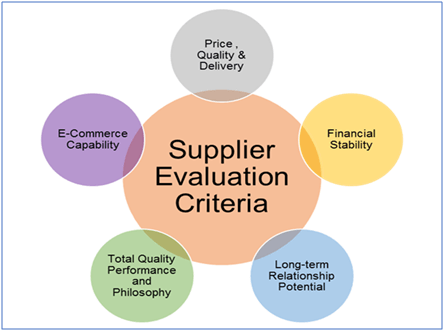
This is the stage to identify potential new global suppliers, the enterprise will develops a detailed list of supplier selection benchmarks, which is used to select the supplier that best meets the requirements. Based on the results of the market evaluation, agents can help to create a final cost model. The operational and economic benefits of the project will then be estimated. RFIs (Request for Information) will then be sent out to the shortlisted suppliers. The RFI will give you information about the capabilities of the suppliers.
The diagram below shows the key stages in preparing for global sourcing.
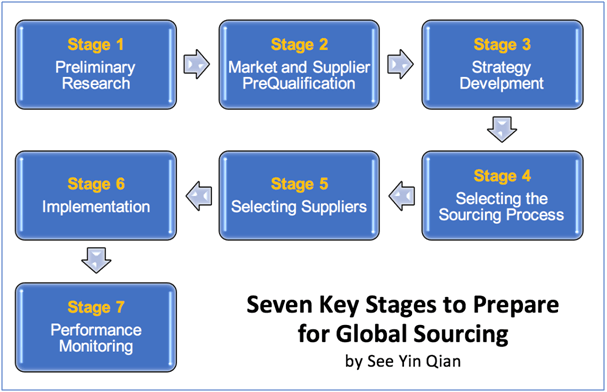
Strategy Development
Deciding where to buy while minimizing risk and costs is how you develop the strategic sourcing strategy. To minimise the risk of untapped opportunities in the market, external forces that are influencing the sourcing category will be analysed. Information about the market, as well as important market players, will be gathered in order to determine the right sourcing strategy for the category and as a corporation. Constantly internal review and act in order will improve and ensure profits.
Selecting the Sourcing Process and Suppliers
During the sourcing process, the common used method is to use a Request for proposal process for soliciting bids. It includes product or service specifications, delivery and service requirements, pricing breakdowns, and legal and financial terms and conditions. The evaluation criteria are usually also stated.
Requests for proposals, analysis, assessment and negotiation are key aspects of strategic sourcing. Supplier candidates will be evaluated on multiple factors that cover everything from CSR to pricing, quality, service and supply capacities. Part of the evaluation criteria are also the ability of suppliers to support the company’s continued growth through business optimization. A technical assessment of the final supply candidate to provide a savings estimate for each candidate. Finally, an implementation schedule outlining timelines for various suppliers is developed.
Implementation
Once the contract is signed, suppliers are expected to support the company in making the implementation phase run as smoothly as possible. Implementation plans vary by degree of change. The communication plan in the strategic sourcing strategy will include any improvements to the specification or process, delivery or service requirements or pricing changes. Furthermore, implementing the contract gives the opportunity to build a supplier relationship and grow it. Similarly, maintain a strong relationship with existing stakeholders by carefully informing how new contracts affect their day-to-day work and what procurement can do to simplify the transition.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Arla Food. (2018). “6-Step Sourcing Process”. Retrieved from https://www.arla.com/company/procurement/sourcing-process/, accessed 01/09/2018.
Guest Contributor. (2015). “Stages of Global Sourcing Strategy”. Retrieved from http://spendmatters.com/2015/09/15/stages-of-a-global-sourcing-strategy/, accessed 01/09/2018.
Lau Chee Leong. (2018). “Eight Essential Steps for an Effective Global Sourcing Strategy”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/eight-essential-steps-effective-global-sourcing-strategy/, accessed 30/08/2018.
Mawson Global, (2015). “5 Benefits Global Sourcing Organisations Can’t Afford to Ignore”. Retrieved from https://mawsonglobal.com/blog/2015/09/21/2015995-benefits-global-sourcing-organisations-cant-afford-to-ignore/, accessed 02/09/2018
Wikipedia, (2018). “Global Sourcing”. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Global_sourcing, accessed 31/08/2018.
Wong Kok Wei. (2018). “Importance of Strategic Sourcing Skill for Effective Procurement”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/importance-strategic-sourcing-skill-effective-procurement/, accessed 30/08/2018.

