Though it sounds simple, the process of procurement is quite complex. It involves sourcing, purchasing, supply chain management, logistics handling, negotiations, risk management and inventory control. This can be simplified by digitalizing the process. Companies that adopt digital procurement solutions can improve the quality and speed of procurement, enhance innovation and reduce risks. Global supply chains are becoming increasingly complicated and integrated and lines between suppliers, customers and other stakeholders are blurring. In such a scenario, companies that can leverage on digital procurement tools will gain a competitive edge over others. On the other hand , companies that are slow or delay to digitize their procurement process, will eventually be outmaneuvered by their more agile counterparts. This article highlights some key technologies to implement digital procurement in an organisation.
Table of Contents
Spend Visibility Analysis Tools
Spend visibility simply refers to traceability and accountability of money in the entire purchase process. It is an organised and detailed system of recording every dollar spent in a purchase transaction. Spend analysis has catapulted procurement from being an irrelevant purchase activity to one of the most important high priority function.
Companies often make the mistake of allocating funds on the basis of inaccurate data resulting in wastage of valuable resources. Spend visibility can highlight procurement categories where excess funds are being directed, more than the value a company derives from it. It puts the spotlight on those projects where the company is bleeding money. Supplier spend analysis can help the company to identify the best deals and prices resulting in better long term relationship with efficient suppliers. It also helps procurement managers to plan and maintain optimum levels of inventory and benefit from economies of scale.
For all this to be done effectively, companies should train its employees and invest in spend analysis software, and ensure that it is compatible with other systems & technologies within the organization.
Blockchain Technology for Smart Contracts
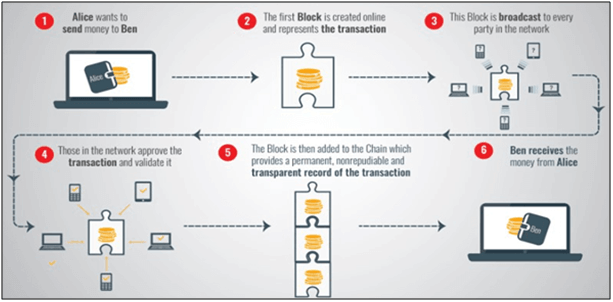
Smart contracts are self-executing transactions that are stored digitally on a block chain. It is a peer to peer trust protocol that allows the performance of a contract without involvement of any intermediary. It is a decentralized system as it does not involve any middlemen, thereby saving time and money. When certain conditions are met and verified, a network of computers will execute the workflow. There is greater efficiency due to high speed and cost reduction. There is also zero error as smart contracts are automated and digitally verifiable. There is no way to dispute the codified terms once smart contract is established. As all transactions on the block chain are encrypted it is almost impossible to hack. With massive investments and greater trust in block chain technologies procurement based applications are gaining greater relevance in recent times. Smart contracts executed through block chain will lead to a cleaner and greener supply chain as all transactions will be authentic, verifiable, traceable and trust worthy. The diagram below shows how blockchain works.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Technology
RPA is a technology application that automates business processes by using business logic and structured inputs. A company can configure software, or a “robot,” to capture and interpret applications for processing a transaction, manipulating data, triggering responses, and communicating with other digital systems using RPA tools. Previously, the procurement team had to manually process the procurement request and create a purchase order. It used to cause delays in issuing a Purchase Order and increased the possibility of errors. With RPA integrated into the procurement process, the team can complete the entire process in a short period of time, from issuing a purchase request to raising a purchase order. RPA assists organizations in managing demand and supply planning from start to finish. It eliminates silos between departments, such as procurement, shipping, warehousing, and inventory management, and manages them as a single centralized team. RPA is especially useful for job-specific tasks such as Work Order Management and Invoice Processing.

Procure to Pay System
The procure-to-pay process, also known as the P2P process, is a coordinated and integrated action taken to meet an organization’s need for goods or services in a timely and cost-effective manner. The steps in a procure-to-pay process must be completed in a specific sequence. The first step is to identify and define business requirements with the assistance of cross-functional stakeholders. Following the completion of the specifications a formal purchase requisition is created. A spot buy can be performed if the requested goods/products have characteristics such as unmanaged category buys, one-time unique purchases, or low-value commodities. Purchase orders that have been approved are then sent to vendors. When the supplier delivers the promised goods/services, the buyer inspects the delivered goods/services to ensure that they meet the contract terms. The supplier’s performance is evaluated based on the data obtained in the previous step. Procure-to-pay implements pay-as-you-go (PAYG) software. It maintains transparency throughout the process, improves supplier engagement, optimizes inventory, and streamlines contract management.
Internet-of-Things (IoT) Technology
The IoT is becoming more prevalent in our daily lives as the number of devices connected to the internet increases. The IoT is a set of technologies and associated business processes that give devices of all kinds the ability to communicate information about their status to other systems, allowing us to evaluate and act on this new source of data. Automation and logistics are central to IoT applications in the industrial sector. IoT solutions are used by energy suppliers to continuously monitor the safety of remote production locations such as oil and gas fields. IoT and big data are inextricably linked. IoT drives big data, providing more information from multiple sources in real-time and allowing for completely new perspectives. The incorporation of IoT technology aids the Oil and Gas, EPC sectors in facilitating connectivity by capturing more data to improve efficiency and safety and security.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Technology
Using smart computer algorithms, AI enables procurement organizations to solve complex problems more effectively. It can be integrated into a variety of software applications, ranging from spend analysis to contract management and strategic sourcing. It is useful in guided buying, chatbot applications, inventory management, error detection and automation of manual tasks. AI incorporates use of new computer technologies that can learn and adapt human behaviour. It is typically designed to solve complex tasks more efficiently than humans.AI has played a crucial role in procurement by providing procurement professionals with additional insights based on extremely complex and large data sets. In its most basic form, (AI) has the potential to drastically alter work practices in even the most complex organizations.
Advanced Analytics for MRO
The emerging field of data analytics, which is currently populated by smaller and more agile vendors, has grown in recent years. A number of exciting technological factors have contributed to this. Among them are the emergence and widespread acceptance of cloud-based business technology, the use of tablet computers in the workplace, and significant advancements in the presentational capability of modern browsers. Employees at all levels are now thinking creatively about how they can leverage corporate data for competitive advantage and demanding the ability to do so on a daily basis. To meet this demand, data analytics and Business intelligence tools fill the void. Most industrial organizations now have massive amounts of MRO data in various forms, which could be a gold mine. New data analytics techniques and cutting-edge BI tools are now being used to “nudge” corporate data assets in order to improve business and bring about fundamental change. MRO activities, along with the massive amounts of transactional data they generate, represent a huge opportunity.
Mixed Reality
In the simulation world, the terms virtual reality and augmented reality are relatively new. The third term, which is gaining popularity, is mixed reality, which refers to the merging or combination of virtual and real environments in which both worlds can coexist. In some circles, mixed reality is also referred to as “Hybrid Reality”. The diagram below shows a team collaborating in mixed reality.

When designing a new product or developing a new product, procurement members and suppliers can benefit from sharing real-world virtual spaces via mixed reality. Buyer representatives, for example, can bring mixed reality devices to a meeting with suppliers. Both the representative and the suppliers can then wear the devices and see the new model as described by the representative. They can then visualize and simulate the product as a result of this. Through such a shared experience, the representative will not only develop stronger relationships with the suppliers, but will also be able to provide a more detailed explanation of the product.
Conclusion
The availability of the above mentioned digital procurement tools has given more teeth to the procurement process. Technology is ever-evolving and, procurement experts should keep up with the rapid pace of digitalization in procurement. Organizations must embrace digital solutions as these will serve as a panacea to solve many procurement challenges. The first step is to identify the procurement objectives, and this is followed by understanding and mapping the available technologies to these objectives. The future undoubtedly will belong to those companies that can leverage on digital procurement solutions to drive better decision making, increase organisational efficiency, assure supplies and successfully mitigate risks.
References
Ashish Deshpande.(2021).“8 Top Procurement Technology Trends for the 21st Century”. Retrieved from https://www.frevvo.com/blog/top-procurement-trends/ accessed 25/09/2021.
Brian Oxenham. (2021).“MRO Data Analytics and Business Intelligence”. Retrieved from https://reliabilityweb.com/articles/entry/mro_data_analytics_and_business_intelligence, accessed 08/10/2021.
Jo Tan Ling Ling, ADPSM. (2021). “Digital Technologies for Major Procurement Projects”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/digital-technologies-for-major-procurement-projects/, accessed 26/09/2021.
Kelly Ho Lay Tin, SDDP.(2021). “Digital Technologies for Efficient Procurement”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/digital-technologies-efficient-procurement/,accessed 26/09/2021.
Kissflow. (2021). “The Ultimate Guide to a Truly Effective Procure-to-Pay Process”. Retrieved from https://kissflow.com/procurement/procure-to-pay-process-guide/, accessed 08/10/2021.
Ma Hwee Na, DPSM.(2018). “Adopting New Technologies for Effective Procurement”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/adopting-new-technologies-effective-procurement/,accessed 26/09/2021.
Sievo.(2020).“Spend Analysis 101 | Comprehensive Guide for Beginners”. Retrieved from https://sievo.com/resources/spend-analysis-101?_sm_au_=iVVDH11VHM4L6NFFMTCVjK7R2J3TF ,accessed 26/09/2021.
Sievo. (2020).“AI in Procurement”. Retrieved from https://sievo.com/resources/ai-in-procurement#what-is-artificial-intelligence-in-procurement”, accessed 05/10/2021.

