The procurement process is not simple and straightforward. Procurement incorporates purchasing planning, supply management, supply-chain handling, sourcing methods, logistics, price negotiation, inventory control, risk management, legal and value analysis. Procurement involves a lot of risk assessment to obtain the best deal from suppliers to boost corporate performance. The manual procurement process is very labour-intensive, time-consuming and consists of a lot of paperwork.
Digital technologies assist procurement in increasing collaboration, analytics and engagement using devices along the entire procurement value chain. This helps to improve workflow, speed, and efficiency. Control expenses with spend analysis, accelerate purchasing with faster order. Leverage technology can eliminate paperwork with cloud-based document management. Reduce human error in invoice evaluation and payment. With the help of technology, it can maintain a complete audit trail and monitor performance with detailed reports. It can be conducted effectively with 360 visibilities and increase the transparency of the whole process.
The key is to analyse how automatization can positively impact the business environment, changing a business’s agility to react and essentially changing its whole value proposition and overall organization.
Table of Contents
The Digitalisation Trend of Procurement
Digital procurement is the application of information and technology to help raise human performance in procurement. It does not require to imply the implementation of new technologies tools. On the contrary, it can suggest how human performance can be expanded using existing devices to help drive better performance expectations, leading to top, bottom-line results. It also implies internal adoption of this change. The use of Cloud, Mobile Technology, Social Media, Big Data and RPA can be leveraged to achieve strategic procurement objectives such as cost reduction, risk mitigation, innovation, and efficiency.
Blockchain Technology for Smart Contracts
Blockchain technology creates opportunities for procurement to improve traceability and security product sourcing and supply chains. Blockchain smart contracts refer to agreement that runs when predetermined conditions are met. It can facilitate smooth transactions where there is no intermediary involvement or time loss. It can automate a workflow, triggering the following action when conditions are met. Only parties who have granted access can use to view contracts, make revision, and accept changes.
These are captured in the block chain record. The blockchain can be programmed to record practically every transaction with shared transparency—the final contracts stored electronically in one location accessible by only the parties who have granted access. Specifically, a characteristic of this type of information storage is that the blockchain data cannot be altered after being recorded, creating evidence for an audit trail from beginning to end, all in one place.
The technology guarantees both data authenticity and integrity. Multiple parties can be shared and collaborate on a contract in real-time and see each other edits even if they are countries apart.For example, smart contracts in the blockchain environment are presently used in crowdfunding, assets transfer and financial services. Smart contracts can likewise be used in medical care and real estate.

Robotics Process Automation (RPA) Technology
Leveraging RPA in procurement is to substantiate this innovative perspective. Errors mar the reason being is manually handling procurement tasks, and it slows down the process, thus caused less efficiency and productivity. RPA and AI can handle both structured and unstructured data. The process is accelerated because requisition can automatically be created and routed to approvers, buyers, and suppliers.
RPA enhance efficiency such as improved data accuracy, reducing operating cost and increased output. Automation tools like advanced AI are out of reach for most businesses. Many businesses take RPA to improve procurement functions. RPA can automate most steps of this process by minimizing human touch points. These incorporate contract management, category management, third-party risk management and supplier relationship management.The survey from the 2020 KPMG report that the global market for robots and AI is expected to reach $157.2 billion. This is well correlated with the top five investment priority all over the world.
For example, an invoicing process is done countless times daily, open an email, open the attached invoice, uncover the relevant information, and enter that data into an ERP. These types of small repetitive tasks are both unremarkable and tedious. The ability to automate can save time for employees to spend on more involved or strategic activities.

Cloud Computing Technology
New technology has introduced another new era of procurement which is based on cloud technology. For procurement, it enables a new level of communication and collaboration that will help keep business costs under control, select the best supplier, enforce company policy, and appraise supplier risk. This decreases the overall amount of manual transaction throughput the entire of the procures to pay cycle.
Technology has transformed the procurement process and revolutionized the way consumers can demand products. With cloud technology, it becomes possible to keep up with the demand even when services are needed around the clock. With these features, it is easy to see why cloud-based platforms from the new business procurement standards are moving towards allowing staff access from anywhere and anytime on any device. It creates transparency from high-level executives and a more spontaneous and coordinated approach to streamline supply chain interactions and the company’s spend culture.
Cloud infrastructure can be designed in three ways.
For example, the cloud allows network-based access to communication tools like emails and calendars. “WhatsApp” is also a cloud-based infrastructure as it comes in correspondence. It is likewise one cloud computing. Everyone send messages, and the information is put away in services providers’ hardware.
Internet of Things (IoT) Technology
IoT in procurement will increase spending visibility and a better understanding of supply and equipment usage. This helps the team improve catalogues content and spend management on what is being used and what is needed. The ability to predict accurately will also improve budget and contract management.
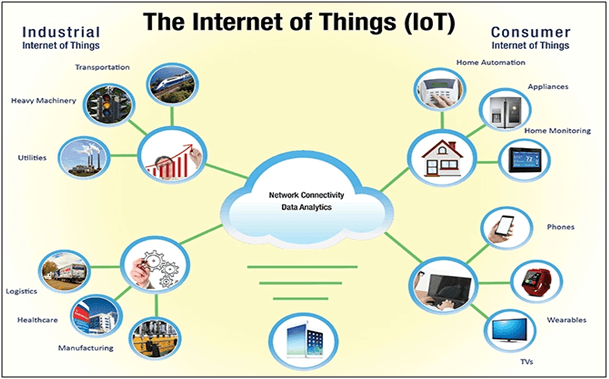
Procurement will be working with more analytics; the IoT optimize the overall cost and improve profitability. IoT can automate much of the processes and gain greater bandwidth and become more strategic in approach. The IoT will significantly improve procurement productivity for the entire organization if it equipped to deal with the analytics gained and make them actionable to the right people. For example, IoT devices are smart mobiles, smart watches, smart fire alarm, medical sensor, fitness trackers and smart security system.
With the environmental impact of operations becoming a significant concern, procurement teams are increasingly looking to reduce carbon footprint. Since one can optimize what one can quantify, IoT data can bring visibility over such processes as transportation. IoT also provides the data that can justify CO2 emissions evaluation and calculate the actual impacts of the emissions reduction initiative. This helps to identify the best solutions for reducing emissions levels and mitigating effects on the environment. Optimizing the shipping solutions to avoid useless detours and stops has proven to minimize bot emission and costs.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
Reference
Atakan Kantarci. (2021). “AI Procurement: Why It Matters And Applications – Use Cases 2021”. Retrieved from https://research.aimultiple.com/ai-procurement/, accessed 04/04/2021.
Chin Pei Sze, ADPSM. (2021). “Digital Procurement For Ship Supplies Operation”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/digital-procurement-ship-supplies-operations/, accessed 04/04/2021.
Cigen. (2020). “5 Real World Use Cases For Robotic Process Automation (RPA) In Procurement”. Retrieved from https://www.cigen.com.au/cigenblog/5-real-world-use-cases-robotic-process-automation-rpa-procurement, accessed 02/04/2021.
Damodar Sahu. (2017). “The Reinvention Of Procurement Through Internet Of Things (IoT)”. Retrieved from https://wiprodigital.com/2017/06/15/reinvention-procurement-internet-things-iot/, accessed 04/04/2021.
Li Gui Li, ADPSM. (2020). “Five Digital Technologies For Procurement Optimization”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/five-digital-technologies-procurement-optimization/, accessed 04/04/2021.
Philip Charles Loges, ADPSM. (2019). “Crucial Digital Technologies Effective Procurement”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/crucial-digital-technologies-effective-procurement/, accessed 04/04/2021.
Raphael Anasthase. (2020). “How Procurement Teams Can Maximize The Benefit From IoT?” Retrieved from https://safecube.com/how-procurement-teams-can-maximize-the-benefits-from-iot/, accessed 04/04/2021.
Ruchi Gupta. (2020). “Are Blockchain Smart Contracts Legally Binding?” Retrieved from https://marketrealist.com/p/which-blockchains-support-smart-contracts/, accessed 02/04/2021.

