The realm of moving goods is currently undergoing significant changes due to digital technologies. Consider the utilization of specialized computer technology, such as blockchain, to display the location of items and ensure their safety. Technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), aid in monitoring goods during transportation. Computers powered by Artificial Intelligence (AI) can determine the quickest and most cost-effective routes for moving items. The concept of big data, which refers to a wealth of information, assists in predicting the required amount of cargo. Additionally, self-driving trucks and drones are contributing to this transformation. The use of cloud technology facilitates seamless collaboration among multiple individuals.

Table of Contents
Blockchain for Transparent Supply Chains
Blockchain technology offers significant advantages in the field of freight forwarding and supply chain management, primarily due to its decentralized and tamper-proof nature. In the realm of freight forwarding, the inability of a single entity to control blockchain records is noteworthy. Altering a record requires control over most of the networked computers, a feat that is impossible in a substantial network. This robustness renders the falsification of information extremely implausible. The sharing of information among various entities within the network is particularly advantageous for freight forwarding. Even if certain computers encounter issues or disruptions, other nodes in the blockchain network continue to maintain the accuracy of records. This redundancy is essential for preserving data integrity, especially in global supply chain systems that are susceptible to various disruptions. Importantly, the tamper-proof design of blockchain ensures that records remain immutable once added. This quality is crucial in freight forwarding, where accurate and unchangeable documentation is pivotal for international shipping regulations and customs procedures. The governance structure of blockchain networks relies on the collaborative efforts of numerous computers, fostering durability and resilience.
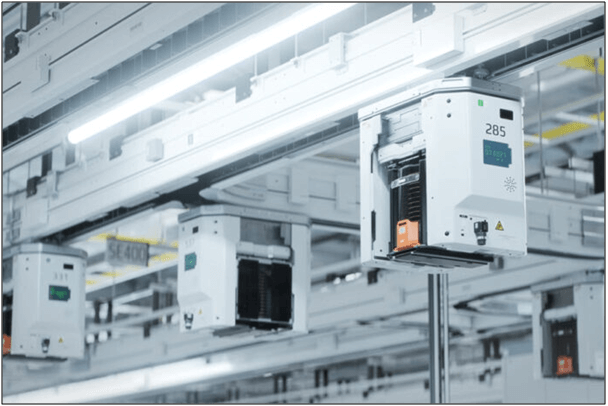

IoT’s role in Freight Transport
In the context of freight forwarding, the integration of advanced automation technologies like pick-by-voice, pick-to-light, and goods-to-human systems streamlines operations, minimizes errors, and enhances customer satisfaction. This harmonious integration with existing equipment and software ensures operational efficiency and adaptability. Simultaneously, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) empower robotics to manage tasks ranging from inventory tracking to order picking, thereby boosting productivity and operational safety. Concerning freight forwarding, the fusion of Internet of Things (IoT) technology offers substantial advantages. By providing real-time insights into shipments, IoT enhances tracking accuracy and predicts maintenance requirements for vehicles and equipment. This constructive collaboration optimizes operational efficiency, reduces costs, and strengthens overall supply chain oversight. The convergence of automation, AI, ML, and IoT transforms the landscape of freight forwarding, making it more agile, precise, and responsive to the dynamic demands of the modern logistics landscape.
Route Planning with AI
In the realm of freight forwarding, urban areas grapple with escalating traffic and logistics challenges due to population expansion and increased vehicle numbers. However, a transformative solution emerges in the form of technology, particularly the capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This innovative force significantly enhances route planning for freight trucks. By harnessing real-time traffic data, AI algorithms adeptly propose optimal routes that skillfully avoid traffic congestion and potential delays. This intelligent approach considers variables such as road closures and delivery timelines, ensuring the creation of streamlined routes that conserve time and curtail fuel expenses. This intelligent integration not only streamlines operations and guarantees punctual deliveries but also aligns with ecological concerns by minimizing the environmental impact. Thus, AI’s mastery in route planning reshapes the freight forwarding landscape, creating a paradigm of efficiency and responsiveness.
Big Data in Freight Management
The influx of data resulting from the convergence of the Internet of Things (IoT) and Information Communication Technology (ICT), known as Big Data, presents opportunities for insights, business value, and revenue generation in freight management. However, effectively managing and analyzing this data poses significant challenges. While Big Data holds the potential to enhance various aspects of freight management, including operations, planning, and infrastructure, its critical challenges require comprehensive examination. Reviews have spotlighted specific applications such as logistics and transportation efficiency. Some have underscored the importance of Big Data in supply chain management, highlighting use cases and research gaps. A comprehensive understanding of the challenges and limitations associated with Big Data is crucial for leveraging its benefits in the dynamic realm of freight management.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.

