As a consumer, we at least encounter one of such incidents as receiving the wrong item, delayed missing shipment, damaged or defective items, etc. If customer service is difficult to reach, refund or replace are delayed, it is unlikely to have satisfaction and trust by consumers again because of the unfortunate incident that happens to them. But on the other side, like an e-commerce business owner, dealing with returned goods or reversed logistics can be irritating and frustrating. But if these complaints left unresolved, it could overwhelm e-commerce businesses.
The infographic below shows an e-commerce fulfillment process.
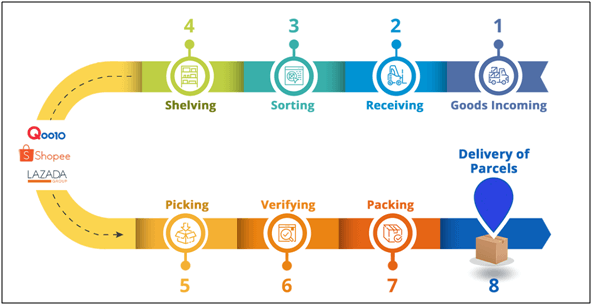
Table of Contents
Understanding E-Commerce Fulfilment
E-commerce fulfillment is defined as the steps taken from receiving, storage, pick and pack, finally ship out to end customer. However, fulfillment can be done by three different types of methods depending on the scale of business that the seller is running.
• Drop shipping is a fulfillment method whereby the customer’s order fulfills directly from the manufacturer or wholesaler. Basically, this fulfillment method, the seller does not keep, store inventory or purchase goods upfront. Instead, the seller will only pay for the goods after the order made by customers. However, using a robust inventory management system is crucial as it will allow sellers and suppliers to have prompt sharing of information.
• 3PL (Third Party Logistics) is an e-commerce fulfillment services provider. E-commerce business owners usually outsource to 3PL service providers when their business expands to a larger scale or overseas. Because 3PL can provide various services such as warehousing, order fulfillment, transportation and many more. Most 3PL have the technologies and knowledge on how to handle this type of business as their profession. A 3PL also can provide small start-ups e-commerce the flexibility to start small yet scaling up when needed.
• Self-fulfillment however, from manage inventory to packing even ship out of customer order in-house by e-commerce seller themselves. This fulfilment method are used by many startups at the beginning of their e-commerce business as the scale of their business might not large but still able to manage on their own.
Picking Strategies
Picking is the process of selecting inventory from storage that to be included in a customer’s order. It is the first thing that happens after the order is placed by the customer and received by the warehouse. After picking, the order is packed – this involves gathering all items from an order and preparing them for shipment to the customer. Below are few picking strategies that can be consider.
• Discrete Order Picking – This picking method is best for small business with low order counts. The picker picks all items for an order at a time by goes to each location and pick each individual item for that order before going back and starting a new order.
• Zone Picking – Multiple pickers are each assigned a different area of the warehouse to pick from. The picker that is assigned to each zone is responsible for picking all the items that located in the assigned zone for each order.
• Batch Picking – this picking method can also be referred to multi-order or consolidated picking. Picker to compile a batch of orders by SKU, one SKU at a time. SKU picked will split later before packing process according to quantity of each order. Orders which require the same SKU are combined into single pick task so that the location is visited once rather than one time per trip. Travelling time is reduced when there are multiple orders with the same SKU.
• Cluster Picking – Each order gets a dedicated box(es) that is usually put on a cart to keep items from different orders separated while picking. This approach prevent picker to go to same location again and allow items to be sorted by the end of picking process.
• Wave Picking – A method that is executed multiple times per day (or shift) and balances more factors than products overlap. Typically, orders are picked one by one without route optimization. Combined orders can be done automatically by WMS/ERP by group according to delivery date, type of orders, customer location, etc.

Designing a Maximum Efficiency Warehouse
The best way to optimize picking process is to design your warehouse for maximum efficiency. This warehousing layout design may depend on how large the warehouse is and how many orders will receive, a significant amount of time that could be wasted walking from one location to another just to fill each order. Here are some tips to keep in mind:
• Place your top-selling products closest to your packing stations.
• Store items that are often sold together in neighbouring storage zones.
• Arrange your inventory from top-selling to low-selling.
Slotting is another storage strategy might consider while designing warehouse layout. This is the process of determining where items should be stored in the picking area based on both its popularity and proximity near to the starting point of picking to reduce travel time. In addition to storing popular items near the picking area, warehouse personnel also want to store items at a height where pickers don’t have to bend down or reach up.
Managing returns
Returns can be annoying, but successful manufacturers and virtual merchants are embracing them because it’s critical to give consumers options. The retail landscape is a battle of low pricing and convenience, and easy returns are a key part of that.
When the returns process quick and easy, customer will you maintain your customer’s trust. Have a system in place that can handle your returns accurately, cost-effectively, and keep your customer experience at the top of the game.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Ajeet Khurana. (2019). “Understanding E-Commerce Third-Party Logistics – 3PL”. Retrieved from https://www.thebalancesmb.com/3pl-ecommerce-logistics-1141740, accessed 12/12/2019.
CatalinZorzini. (2019). “Ecommerce Fulfillment (December 2019): The Best Order Fulfilment Companies”. Retrieved from https://ecommerce-platforms.com/articles/ecommerce-fulfillment-best-order-fulfilment-companies, accessed 12/12/2019
Doreen Teng, PDLM. (2019). “Integrating Key Logistic Practices for Effective Digital Commerce Health”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/integrating-key-logistics-practices-effective-digital-commerce-health/, accessed 14/12/2019.
Jonathan Goh Seng Kim, DLSM. (2018). “Key Strategies to Improve Warehouse Space Efficiency”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/key-strategies-improve-warehouse-space-efficiency/, accessed 14/12/2019.
Kristina Lopienski. (2019). “How to Fulfill Orders Yourself & What Challenges to Look Out For”. Retrieved from https://www.shipbob.com/blog/self-fulfillment/, accessed 13/12/2019.

