In the early 2010s, machine-to-machine innovation, or M2M technology, has matured with the advancement of communications, such as RFID, Wi-Fi, and cellular network. Sensors could be deployed to allow communications between different mechanization parts to support operations decisions.
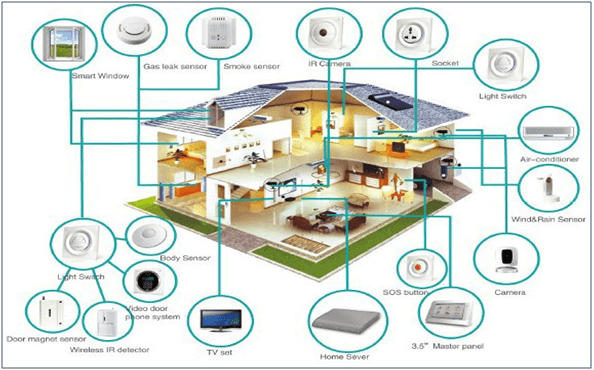
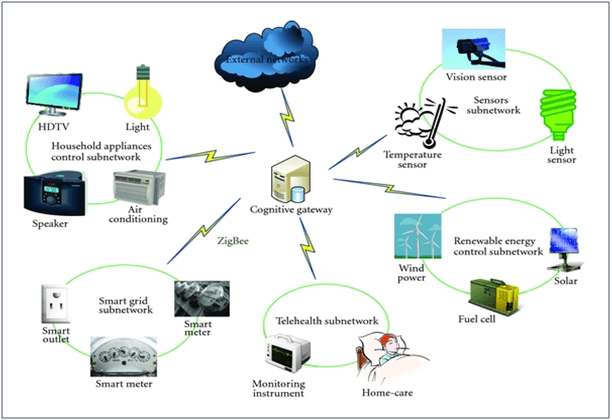
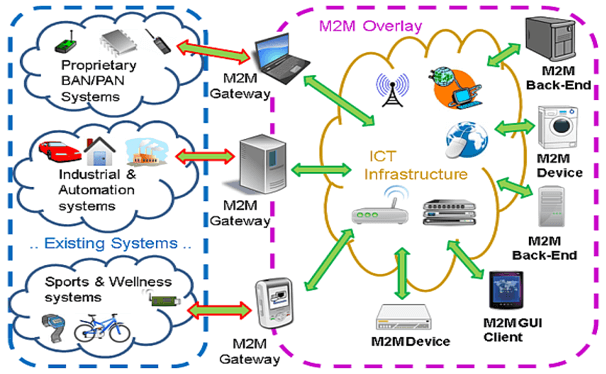
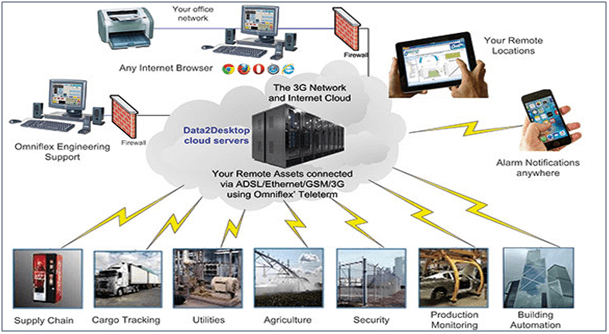
The advancement and integration of communications and machines facilitate M2M system to gain better control over hardware operations and allow for intelligent operations decision-making. The automation of massive data collection and exchange, also greatly improves situation awareness and facilitates the development of operational strategies. The diagram below illustrates the potential applications that could benefit from the use of M2M technology.

Table of Contents
M2M Application for Logistics
The logistics industry has greatly benefited from the M2M technology, as tracking and monitoring of mobile assets and fleet management has become a possibility with the availability of a wide range of connectivity options from satellite and cellular networks, including Satellite Messaging.


Key Advantages for M2M Application
- Increase manufacturing productivity:
With better visualisation and analysis of demand or consumption patterns, manufacturing supply could be adjusted and goods distribution flow could be optimised to better meet demand.
- Optimise logistics with data analytics:
With the availability of digital technologies such as sensors on transport fleet, network routing engines and delivery optimisation service on digital maps e.g. Google map, smart routing and fleet distribution could take into consideration the fleet capacity, storage and delivery locations, traffic and road conditions, to greatly reduce manpower and transport costs and improve efficiency.
M2M Application for Utilities
Keeping utilities (power, water and gas) costs down are a priority to both the home user as well as the business consumer. With the exponential rise in utility demands globally, utility distribution is not just an expense, but a sustainability issue. An intelligent utilities distribution network provides solutions to enable the automated interaction amongst devices to respond to critical events or motorise utilities flow in the system to meet a sudden spike in demand, improve efficiency and reliability in utility distribution, optimize manpower and energy resources, and asset maintainability.Smart Metering Readers (AMR) is an innovative digital utility meter that records real-time utility consumption for power, water or gas, to facilitate analysis of consumption patterns. This would also help provide a more reliable and sustainable supply monitoring.Solar and Wind renewable energy engineers use sensors and M2M technology to assess and monitor energy production levels, analyse them against energy consumption patterns, to reduce the dependency of other sources to augment energy demands.Oil, Gas and Petroleum engineers could centrally monitor and access their remote sites, through the implementation of remote sensors, controllers, and instrumentation at pipelines and wellheads.
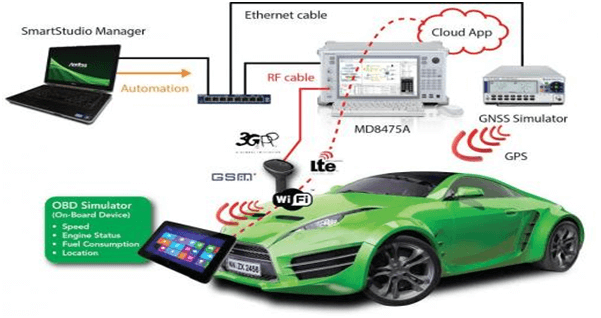
M2M Application for Automotive
Embedded GPS receiver provides the location of the fleet vehicles, and road construction trucks and trailers vehicles and transmit this information through the cellular network via eSIM to a central monitoring system. Some trucks are also embedded with Wi-Fi sensors to transmit data at truck stops or other available Wi-Fi hot spots. Besides locating the vehicles, sensors are also used to track the speed, usage, and other critical factors, such as refrigerated truck temperatures, humidifier level and driver hours alerts.
Coupled with the maturity of M2M technology augmented with LiDAR technology, 5G technology, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technology, vehicles could make automated and intelligent navigational decisions, which facilitates the development of autonomous or driverless vehicles. With its maturity, this would be a transformational change to the logistics and service industry.
M2M Application for Security
Cameras no longer need to be permanently fixed to a wall due to the availability of traverse visual data from gadgets like mobile phones and tablets. Given the opportunity to move the camera to any angle or position you require whilst maintaining the ability to access live-visual data. With this solution can be taken likes of traffic agencies by mounting CCTV cameras to a vehicle. Real-time visual and capture data can be received of any location or angle you could ever need. This technology improves fleet security and protection, as it records (and still have proof of who’s liable) without recording every second while the driver is in the vehicle. This reduces the cost of unnecessary data storage by having to store hours of footage, instead, it will only keep clips you need.

M2M Application for Remote Monitoring
Remote asset monitoring and management are possible when data related to assets could be remotely streamed over the network and internet cloud. This will also facilitate providence of integrated monitoring and management services 24/7/365 from anywhere around the world thru VPN connection. The main advantage is that it reduces downtime and improve business process, thus providing greater efficiency and higher revenues return. Additionally, managing assets in real-time provide a competitive advantage for the company.
M2M Application for Robotics
Robots are more effective than humans when carrying out tasks that are hazardous to human health, repetitive tasks, that require high precision or are too laborious. While robotics technology has been available in the market, the adoption rate was slow then, due to concern of high setup costs, maintenance and upgrading costs. There is also fear of accidental damage or lost, e.g. robots were locked away until they are specifically requested or worried about being stolen or broken.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Abi Teh Ching Yee, ADLSM. (2019). “Autonomous Devices for Digital Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/autonomous-devices-for-digital-warehousing, accessed 22/06/2019.
Alex Lim Tze How, DLSM. (2020). “Technologies for Global Logistics Services”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/technologies-global-logistics-services/, accessed 29/06/2020.
Ee Soon Sern, DLSM. (2018). “Autonomous Mobile Robotics for Effective Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/autonomous-mobile-robotics-effective-warehousing, accessed 15/03/2020.
Malvina Ong Moy Geem, ADLSM. (2019). “Digital Technologies for Fleet Visibility and Responsiveness”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/digital-technologies-fleet-visibility-responsiveness/, accessed 29/06/2020.
Surendran, DLSM. (2018). “Adopting New Technologies for Effective Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/adopting-new-technologies-effective-warehousing, accessed 11/9/2018.

