Warehousing is in the midst of a tech-driven revolution as companies race to identify and adopt emerging technologies that cut costs, optimize operations and improve overall supply chain efficiency. In some of the largest economies and companies, warehouse drones and robots already have been employed.
It’s not just logistics giants who are adopting innovative tech-based solutions. With the cost of automation falling, increasing numbers of SMEs and start-ups are investing in these efficient technologies. This article discusses the top nine technologies that are shaking up the traditional warehousing scene.
Table of Contents
Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS)
Automated storage and retrieval systems have been around for years, and though they have done their job of improving throughput and accuracy, they have often been regarded as being expensive, clunky, and generally inflexible. Having said that, today’s AS/RS’s are only getting sleeker and still out all of their original benefits–reduced labor costs/restraints, modular possibilities, and, of course, increased accuracy. You do not need to complete a comprehensive overhaul of your warehouse to make it smarter and more efficient; instead, introduce the technologies that make sense for your business and all of its processes first. Then, you will see that any warehouse can become a “smart” warehouse.

Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
There is no better way to ramp up your storage and retrieval processes than to integrate automatic guided vehicles, otherwise known as AGVs, into your warehouse.
The structural integrity of AGVs are evolving as technology moves forward, but even the models that have been on the market for some time have proven to be safer and yield a quicker ROI than manual labor. Some of their most important functions include pallet, rack, and other container storage, and even functions that control and automate the entire receiving process.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems, otherwise known as WMSs, are comprehensive software systems that wrangle all of your important data into one platform that can be easily accessed by internal players as well as any chosen members of your supply chain.
This compartmentalizing of data makes for lightning-fast reporting which, when used tactfully, can mean uber-efficient planning, even for the scenarios that you do not see coming. All in all, the use of warehouse management – or warehouse execution – systems perfectly complements other automated elements.
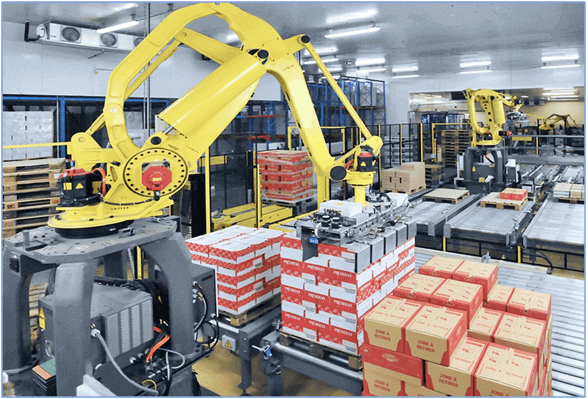
Robotic Palletizers
Robotic palletizers were introduced in the early 1980s and have an End-of-Arm Tool (EoAT) to grab the product from a conveyor and position it onto a pallet. The EoAT is often custom-designed to handle one or more specific products.
Robotic palletizing systems are capable of dispensing and conveying pallets, metering cases on the product infeed and utilizing robotics to palletize cases and apply slip sheets where required. Additional components of a robotic palletizer are infeed conveyors that deliver products to the robot, pallet dispensers that automatically deliver a single pallet to the robot from a stack of pallets, and outfeed conveyors that take pallets with full stacks away from the robot.
These solutions also employ automatic slip sheet or tier sheet dispensers and safety devices such as fencing and light curtains. At the end of most palletizing systems is an automatic stretch wrapper. Douglas will purchase and integrate most stretch wrappers.
Automatic Stretch Wrapping Machine
Packaging is the final step of your production line, but the first thing that your customers see after your products are delivered. Efficiency and consistency are the two most important elements of any successful packaging.
Good stretch wraps will protect your pallets from dust, damage and other forms of tapering. Although wrapping pallets isn’t complicated, hand stretch wrapping causes inconsistencies. Companies are now finding it easier to invest in stretch wrapping machines that can comply with their unique daily operations.
Picking Robotics
Automated warehouse picking is the implementation of robotic or semi-robotic technologies that enhance the work of human pickers. Though there is a wide range of options to choose from in the realm of automated warehouse picking, the most efficient automation tools work with your team members and can be easily integrated into existing warehouse processes quickly and seamlessly.
Automated warehouse picking can also reduce the walking time and shorten picking routes, integrate with your existing WMS and support accurate picking and packing. It can be used in a broad spectrum of industries, including e-commerce, manufacturing, retail, transportation, food and beverage, medical equipment and more.
Drone Technology
Drone technology is more often associated with outside activities. However, drones can also be used internally to a business, such as in a warehouse. Technologists have developed a system that allows aerial drones to read RFID tags tens of meters away.
The technology comes from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and it could save retailers billions lost through faulty inventory records. The drones have been equipped to read radio-frequency identification (RFID) tags from tens of meters away while identifying the tags’ locations. The equipped drone system has the potential to be used in large warehouses in order to prevent inventory mismatches and locate individual items.
RFID Technology
RFID is an acronym for “radio-frequency identification” and refers to a technology whereby digital data encoded in RFID tags or smart labels are captured by a reader via radio waves. RFID is similar to barcoding in that data from a tag or label are captured by a device that stores the data in a database. RFID have taken away much of that administration effort, by allowing operatives to simply scan a pick face and enter picked quantities on a keypad. More advanced solutions even eliminate the data entry altogether, leaving the operative to concentrate solely on the actual picking. Scanning technologies have had a similar impact in other areas of warehouse operation, such as receiving, put-away, and dispatch.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Agility (2019). “9 New Warehouse Technologies”.Retrieved from: https://www.agility.com/en/technology-news/warehousing-on-the-edge-9-new-warehouse-technologies/, accessed 15/03/2019.
Ann Chong Fong Ting, DPSM. (2018). “Warehouse Technologies for Effective Inventory Control”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/warehouse-technologies-effective-inventory-control/, accessed 15/03/2019.
Fergal Glynn. (2019). “What is automated warehouse picking?” Retrieved from: https://6river.com/what-is-automated-warehouse-picking/, accessed 15/03/2019.
Helmi Salleh, ADLSM. (2019). “Autonomous Devices for Digital Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/autonomous-devices-digital-warehousing/, accessed 15/03/2019.
Jill Lahman. (2018). “Robotic Palletizers: What Are They & How Do They Improve Productivity?” https://www.douglas-machine.com/robotic-palletizers-what-are-they-how-do-they-improve-productivity/, accessed 15/03/2019.
Mat Bedard. (2017). “8 Benefits of Using an Automatic Stretch Wrapping Machine”. Retrieved from: http://www.planautomation.com/blog/8-benefits-of-using-an-automatic-stretch-wrapping-machine, accessed 15/03/2019.
Shelly Stazzone. (2019). “7 Smart Warehouse Technologies to Implement Today”. Retrieved from: https://www.camcode.com/asset-tags/smart-warehouse-technologies/, accessed 15/03/2019.
Tim Sandle. (2017). “Using drones in large warehouses to prevent inventory mismatches” Retrieved from:
http://www.digitaljournal.com/tech-and-science/technology/using-drones-in-large-warehouses-to-prevent-inventory-mismatches/article/504812, accessed 15/03/2019.

