With the world market demand growing, freight logistics have always been one of the vital elements that help various sectors to function. The freight logistics of these companies must be equipped with the latest data and technologies to provide an efficient logistical service to their customers. Future technologies of freight logistics like robotics programming improve delivery capabilities. It contributes to the efficient analysis of data in the logistics field by generating and transmitting data. The Real-Time Location System is an example, it allows better tracking of products during transportation wirelessly through motion sensors and tags. The use of smart technology for freight logistics refers to automating various aspects of logistics operations. Companies work to achieve increased productivity and efficiency of transportation which contributes to lower operating costs. This article discusses some smart technologies for efficient logistics and transportation.
Table of Contents
Digital Technology for Transport Efficiency
Digital Transport refers to advanced applications designed to provide creative and specialized services for different modes of transport and traffic management, allowing users to get better information, and also making transport networks safer, more effective, and productive. It often refers to two application areas, Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS) where it is implemented in the field of road transport, including infrastructure, vehicles, and users, traffic and mobility management, as well as intermodal transport, a sustainable transport alternative, which refers to technological solutions used in transport systems for better efficiency and also to be environmentally, socially and economically sustainable in the communities they serve.

Digital business operations require digital supply chains. Digitization, transferring from the use of manual to devices and machines is efficient as the processing of data is much quicker. Profound digital transformation is occurring in many areas and it challenges the status of the different companies. The emergence of digital technology is affecting the systems of logistics transportation in the supply chain management positively. Due to higher mobility demand, challenges like financing, volatile oil prices, and dealing with emissions are surfaced. Decision-makers of policy and planning have to address these issues, as well as try to develop a transportation system capable of fulfilling the future needs of society and the economy. Innovative uses of technologies in areas such as data analysis, the Internet of Things, and the cloud are creating competition among the existing companies.
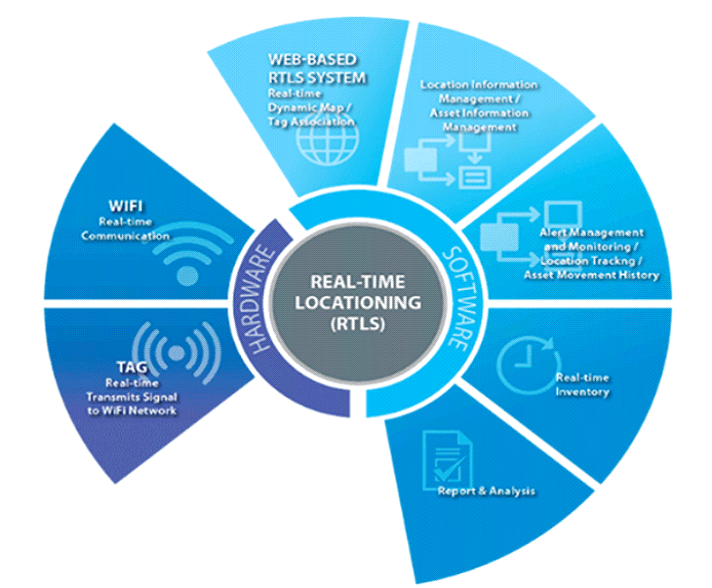
Tracking Delivery Efficiency
The Real-Time Location System (RTLS) incorporates technology that is capable of identifying and tracking the geographical location of objects and humans in real-time. Generally, RTLS is implemented within a building or facility area. A wireless Real-Time Location System tag will be connected to the object during delivery or worn by personnel, the signal transmitted from the tag is received by one fixed point of location from a unique tag. RTLS includes location sensors, battery-operated tags, application software, and network infrastructure.
Autonomous Technologies for Freight Efficiency
In the freight industry, digitalization has always been a slow but unavoidable process. A significant difference can be observed when comparing the vintage shipping of the past to how it is carried out currently. There are now fully automated port terminals, autonomous ships, freight benchmarking services, proposals of a floating warehouse, use of drones for cargo deliveries, and software developed to suit and bring the best out of the companies’ operations. Digital technologies revolutionize freight shipments, improving the efficiency and performance of shipments for better transportation. Digitalisation also allows better management of different shipping processes as different factors can be measured with better proficiency. Logistics network optimization is ineffective without integrating performance measurements, analysis, and feedback. Output affects behaviour that impacts supply chain performance.
Digitalisation brought about new measurement tools and software that easily determines and classifies the information as per the requirement. As such, integrating these can improve logistics network optimization. These metrics are Cycle time, Cost, Service/quality, and Asset. Development of Global logistics metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) are being carried out and implemented to score-card LSP (Logistics Service Providers) performance as well as to align payment terms to these metrics. Improvisation is done with the help of generous feedback from employees. Thus, the ideas and suggestions of the employees should be recorded periodically. This ensures that ideas are generated and at the same time, revealing any flaws in the system.
Robotic Process Automation for Logistics Efficiency
In the age of automation, technology plays an essential role in raising the efficiency of an organization. Machines in a value chain are connected and disseminate crucial information and data based on common standards. This meant that human participation in the process is close to zero as humans play the role of monitoring and supporting automation. The evolution of Automation Technologies has improved significantly for Logistics Service Providers, use of machines helps companies to give high satisfaction to customers. The technologies collaborate closely with one another to improve productivity and efficiency, reducing the need for manpower, as well as reducing the tendency of errors.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Aidilhaswin Hassan, DLSM. (2021). “Smart Technologies for Efficient Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/smart-technologies-efficient-warehousing, accessed 13/06/2021.
Cyrus Calvin dela Cruz, ADLSM. (2019). “New Technologies to Manage Freight Shipments”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/new-technologies-manage-freight-shipments, accessed 13/06/2021.
Gharu Mandeep Singh, DLSM. (2019). “Essential Considerations for Digital Transportation in Logistics Chain”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/essential-considerations-digital-transportation-logistics-chain, accessed 13/06/2021.
Goh Siang Wei, DLSM. (2020). “Technologies for Warehouse Automation”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/technologies-warehouse-automation, accessed 13/06/2021.
Kelvin Hoi Kar Wai, DLSM. (2018). “Autonomous Vehicles for Digital Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/autonomous-vehicles-digital-warehousing, accessed 13/06/2021.
Mohamed Farouk Bin Jailabdeen, ADLSM. (2021). “Digital Technologies for a Smart Warehouse”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/digital-technologies-smart-warehouse, accessed 13/06/2021.
Ng Song Heng Andy, DLSM. (2020). “Real-Time Location System for Distribution Logistics”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/real-time-location-system-distribution-logistics, accessed 13/06/2021.


