The digital future is re-shaping the real estate industry. It is of vital importance for the real estate industry to pursue digital environment to meet the changing customer preferences and engagements, building and information security, cost efficiency and increased competition.
Digital technologies will change the IT landscape in the real estate industry. The consumer journey in digital commerce enriches our daily lives with each advancement in technology. Digital commerce is the core of innovations in customer experience that support business models and technology as it is getting more visual, conversational and intelligent. This article highlights the technologies and trends that will have an impact on the real estate digital commerce in the coming years.
Table of Contents
Visual Experience
Consumers research revealed that users increasingly see the property search as a mobile experience. The future of property discovery must be a visual experience in a virtual 3D model, rather than one only involving the keyboard. Smartphone technologies and the Internet of things (IoT) will provide a new wave of smart buildings and other visual processing VR and AR are enabling buyers to scan properties.

Conversational Commerce
The growing usage of mobile messaging applications such as Chatbots, WeChat, Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp witness an explosive growth for consumers to discover goods and services via a dialogue (for example, when booking a hotel). Autonomous chatbots tools in real estate can be deployed in the above applications to assist in responding to consumers’ common questions. Potential consumers would also be able to browse through the many options with more savings to look for the right deal.
Big Data and Real Estate Data Analytics
Businesses and consumers can gain by recognising big data analytics. Big data analytics is the process of examining data to predict and prescript about the information they contain and techniques to enable real estate companies to optimise customer database and make better marketing decisions.
• Descriptive analytics uses data from large amounts of sources over a specific timeline to describe trends such as consumer preferences to match the home buyers’ needs that occurred over the years.
• Diagnostic analytics uses historical data to understand what happened in the past. Patterns in the analysis highlight opportunities for different pricing based on willingness to pay.
• Predictive analytics utilizes descriptive and diagnostic analytics to recognize to forecast how much rent is likely to increase in the future.
• Prescriptive analytics aims to predict testing strategy outcomes and determine the best course of recommendations such as ensuring positive cash flow in the future.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) for the Real Estate Industry
AI is the process by which the ability of software algorithms to execute tasks that think like an intelligent human mind. AI has the capability to transform many decisions making, offering advanced technology to calculate future sell and rent prices, identify market analysis and pinpoint opportunities. AI reduces waiting time and cost savings in streaming transactions process for real estate operations. There are three useful real estate levels, ranging from automating tasks to taking independent decisions.
The first level is the automating routine and is done by creating tailor-made sets of data that a lead provides an estate professional such as a client’s preferences and previous interactions. Data driven is what yields insight to get more generic findings, which worked well for similar past clients. AI is able to help optimize real estate databases and offer recommendations.
Implementing this is necessary because recommended searching real estate database engines are becoming long and tedious. A smart system would be the ideal search method, finding the right offers for the client’s budget and interest.
The next level is supporting and assisting human-led process. Employing Big data, investors are able to get accurate market movements and trends with potentially popular properties. Likewise, smart contract in blockchain technology simplify the rental transactions and eliminate papers contract savings money in the process.
The last level is autonomous intelligence chatbots, drones and robots, which requires no human intervention.

Virtual Reality (VR) for the Real Estate Industry
Virtual reality headsets connect with a smartphone can provide 360-degree virtual reality property tours. The uses of virtual reality device go beyond entertainment and enables consumers to view the interior of a property in a remote location. This improves consumer experiences making it a perfect marketing tool to enable home tour for buyers and sellers without actually going to the physical site.
Augmented Reality (AR) and 3-D Printing
AR keeps smartphone user engagement. Users could simply click and adjust based on their desired style and furniture, offering them the capability to check how the items works with that space. Just walking down the street and holding the phone one can find the property for sale and see the price. Consumers can explore the AR catalog with real-time 3D print adding big buildings and floor plans. AR will be a great practice within the real estate sales in the coming decade. Several real estate agencies have already integrated AR features into their mobile apps and gaining benefits.
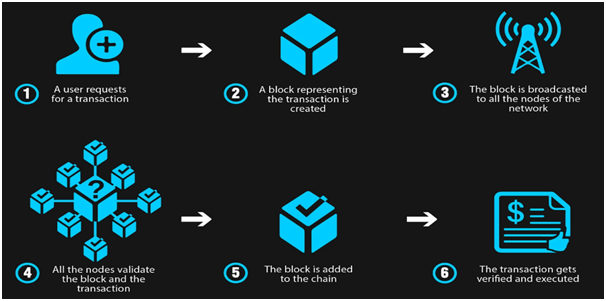
Blockchain for Smart Contracts
Smart contract is connected with blockchain technology. A block is a set of transactions that have been verified and every transaction would be added as the next link in the chain. Once a block is written in the ledger, it can no longer be changed. Every member of the users will get a fair distribution of their payment. Singapore-based real estate online platform Averspace makes it easy for homeowners and tenants to directly enter into major transactions such as digital tenancy agreement secured by blockchain without centralized authorities.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of things (IoT) refers to all devices that are connected by the internet and applications which communicate with each other via sensors, software and network. A major shift has been noticed in real estate to enhance the way consumers perform their daily chores and make their lives easier. In Singapore and Thailand, living in the digital age where individuals are driven by having the world at their fingertips, convenience often presents itself in the form of a smartphone. SMART (Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology) home system could sense the optimum usage temperature and lighting and has impact on energy efficiency.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Anatoly Khorozov (2017). “Trends Driving the Chatbot Growth”. Retrieved from https://chatbotsmagazine.com/trends-driving-the-chatbot-growth-77b78145bac, accessed 19/09/2019.
Charles Mburugu (2019). “Real Estate Data Analytics is What You Need to Get Rich” Retrieved from https://www.mashvisor.com/blog/real-estate-data-analytics-get-rich, accessed 21/09/2019.
Danish Wadhwa (2019). “AI will impact and Disrupt the Real Estate Industry in A Big Way”. Retrieved from https://www.evolving-science.com/intelligent-machines-artificial-intelligence/ai-will-impact-and-disrupt-real-estate-00953, accessed 10/09/2019.
Jasmine Morgan (2019). “Why Real Estate Needs to Step Up Its AI Game”. Retrieved from https://www.bbvaopenmind.com/en/technology/artificial-intelligence/why-real-estate-needs-to-step-up-its-ai-game, assessed 14/09/2019.
Joe Qiao Zihui, ADPSM. (2019). “Current Applications of Blockchain Technology for Global Supply Chain”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/current-applications-blockchain-technology-global-supply-chain, accessed 14/09/2019.
Josh H, Mike M, Ad B, Avishek B (2017). “Digital trends in real estate, hospitality and construction”. Retrieved from https://www.ey.com/Publication/vwLUAssets/ey-digital-trends-in-real-estate-hospitality-and-construction/$FILE/ey-digital-trends-in-real-estate-hospitality-and-construction.pdf, accessed 10/09/2019.
Richard Hartung (2018). “In Blockchain We Trust”. Retrieved from https://www.psd.gov.sg/challenge/ideas/deep-dive/blockchain-trust-public-service, accessed 14/09/2019.
Shereen Chan, PDPM. (2019). “Four Key Digital Technologies for Data Centre”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/four-key-digital-technologies-data-centre, accessed 21/09/2019.
Susan Moore (2018). “Top 10 Trends in Digital Commerce”. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/top-10-trends-in-digital-commerce, assessed 13/09/2019.

