Pharmaceutical logistics is demanding, complex, and unlike any other industry. For biopharmaceuticals, a reliable, temperature-controlled supply chain is essential to save lives. Cold chain is the supply chain for cargo that requires end-to-end temperature control throughout transit. An uninterrupted cold chain is a set of warehouse operations that maintain a specified temperature range (e.g., two °C to 8°C) for transporting sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and biological materials. A broken cold chain can result in product damage, loss of integrity, or, worse, patient harm. Demand for healthcare products means logistics service providers increasingly see opportunities to offer pharmaceutical cold chain logistics solutions. This article focuses on the fundamental characteristics that make the healthcare sector function smarter, better, and more efficiently.

Table of Contents
Cold Chain Monitoring Using Telematics
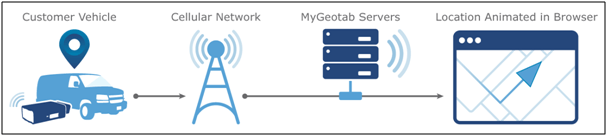
Telematic detectors measure the temperature and humidity of materials. It also can determine and reports whether the temperature of specific goods is consistently above or below the ideal temperature. It allows companies to find a place in their temperature-controlled supply chain (or cold chain) to maintain their preferred quality. Telematics technology for cold chain management gives fleet managers greater control over their fleets by monitoring the exact location of vehicles, allowing drivers to see specific temperatures of refrigerated goods to save high costs. A personalized cold chain management system provides a detailed history of consumer temperature through the most dynamic cold chain from processing, cold storage, intermodal storage, and point of use. With telematics technology, the pharmaceutical industry can track goods and monitor environmental conditions throughout the supply chain.
Cold Chain Active
An active cold chain refers to a truck-mounted refrigeration unit that maintains a constant temperature throughout the cargo compartment. Refrigerated trucks, also known as ‘Reefer’, create a conditioned environment within the truck to protect the contents from outside temperature changes. Such trailers often feature caulked walls, heavy-duty door seals, and even reflective panels to block the sun’s rays and prevent the materials inside from rotting, deteriorating, or being damaged. Cold-chain transport is preferable for temperature-sensitive products such as pharmaceuticals and perishable products such as meat, milk, flowers, and live tropical fish. The International Air Transport Association defines “perishable” materials as those that degrade over time when exposed to certain conditions. Fine art, flowers, and pharmaceuticals are examples of non-perishable refrigerated cargo.
Components of a Cold Chain Operation
Cold chain logistics is the technological process that ensures the transportation and integrity of temperature-sensitive products and goods along the supply chain. A successful cold chain operation consists of the refrigeration system, the refrigerated storage and shipping, as well as the cold processing and distribution. The refrigeration system enables perishable goods such as food at the right temperature in all aspects of the supply chain, including processing, storage, and transportation. The refrigerated storage provides facilities to hold merchandise for a specified period before shipment to a designated market or intermediate location for processing and distribution. The refrigerated shipping ensures the availability of shipment’s arrival while maintaining constant temperature, optimal humidity levels, and integrity. The cold processing and distribution provides resources to process goods with good hygiene and consolidate shipments using shipping crates, crates, and pallets.
Monitoring and Tracking of Temperatures
Pharmaceutical supplies require temperature regulated logistics since damaged pharmaceuticals can pharmaceutical supplies require temperature-regulated logistics since damaged pharmaceuticals can have severe consequences for a patient’s health and well-being. Different products have different maintenance temperature needs to ensure product integrity across the supply chain. The cold chain sector has defined temperature standards to suit most products. Temperature-controlled logistics includes storing, preserving, and transporting goods that are temperature sensitive and must keep at a specific temperature. This is especially crucial for pharmaceuticals since rotten medications can lose effectiveness and significantly affect the patient’s health and well-being. Because of the consequences of improperly kept drugs, regulator standards have gotten stricter, and pharmaceutical firms must be able to demonstrate that their goods have been handled through cold-chain logistics.
Preparation of Cold Chain Shipments
Cold chain devices maintain a constant temperature rather than create shipments at that temperature. For example, if a shipment has been exposed to extreme heat or cold during transit, using a self-powered refrigerated container can alleviate these concerns. The loading unit that transports the cargo must also remain adequately prepared. A refrigerated container, for example, should be steam-cleaned to eliminate the risk of bacterial contamination while maintaining the temperature and humidity conditions specified by the shipper. The next issue is atmospheric control, which involves maintaining appropriate oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, which helps to delay the ripening of fruits such as bananas. Polyethylene bags, for example, will aid in controlling how gases permeate throughout the transportation process.

Conformity of Cold Chain Shipment
The cold chain is essential for food preservation and the prevention of foodborne illness. Depending on customs formalities at the destination of arrival, forwarders and individual customers may need a permit from a food governing body or an import license. Food safety during transit is critical, according to stakeholders worldwide, including researchers, standard-setting organizations, regulators, and industry leaders. However, legislation varies significantly across countries regarding food safety and public health. Food laws seek to incorporate best practices in food safety in response to distribution, technological innovation, and knowledge changes. Therefore, it is important to be aware of country-specific customs regulations when shipping food that requires special shipping.
Freezer Warehouse Automation
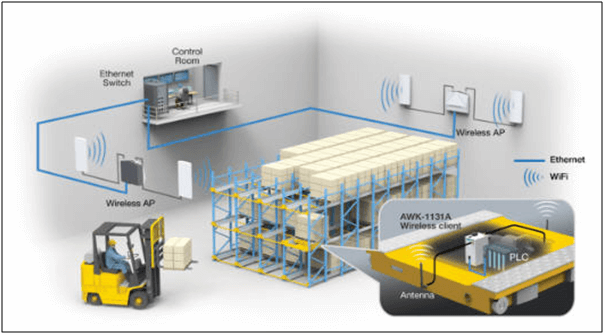
Automated Storage Retrieval Systems are modular subsystems that are easily replaceable to reduce downtime and extend the overall system’s service life. They give users better inventory control and tracking and more flexibility to adapt to changing business conditions. With AS/RS systems, businesses can significantly save inventory storage costs due to vastly improved warehouse space utilization creating greater storage density. They also reduce labor costs by lowering workforce requirements, improving workplace safety, and removing employees from hazardous working conditions (such as cold food storage environments).
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.

