Suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors should consider capitalizing on process automation. Robotics Process Automation or RPA are being introduced for warehouse modernization. RPA is a software technology that allows the business to automate low-level tasks in the future, as technology improves. Using robots and machine which imitate human actions in doing repetitive operational tasks previously completed by humans. It is used not to replace business processes but to process much better.
RPA is the fastest growing automating processes for today’s digital marketing. This automation process is being described to perform warehousing process including picking, sorting, packing, retrieval, storage, loading and unloading is done by employees. But what will be the impact of this Robotic Process Automation?
Table of Contents
Faster Operations and Improve Product Consistency
This article already touched on one of the main benefits of warehouse automation: speed. No matter how well a person memorizes a warehouse, they still can’t beat an automated system that instantaneously identifies the locations of all of the items in a given order. These systems can also find the optimum route to collect them, maximizing productivity during the product retrieval process.
Using robots has enabled warehouses to maximize efficiency and get products or needed items out the door in a much faster way. A single robot can perform the task of multiple humans in less time and less prone to errors than humans. From damaged products to wasted materials, mistakes common in production can be thwarted with a strategic introduction of automation.
Robots are tireless, they can work 24 hours a day, 7 days a week or continuously depending on the order of necessity. It can move up to 500 pallets per hours. Loading and unloading is easy using robots, provides smooth movements at varying speeds and capable of handling different pallet sizes, types and weight.
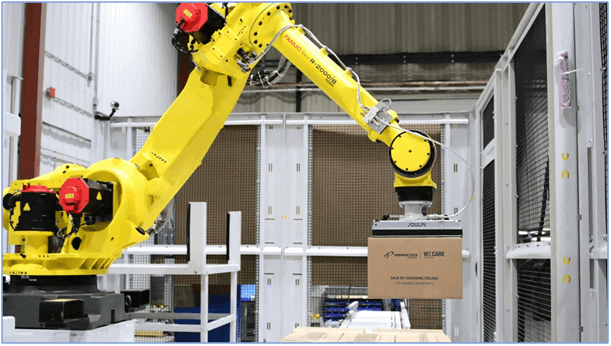
End-to-End Packaging Automation
Food packaging robots have been incorporated into parts of the food supply chain for some time, but only recently have robotics become advanced enough to automate the entire packaging process from end to end. This means a shift to robotics across every conventional touch point in a facility, from de-palletizing and unpacking to primary, secondary and tertiary packaging. This is particularly evident in quality control. Bottle filling, for example, has historically required human involvement to individually inspect incoming materials before the filling process and then examine the final product afterward. With robotics, however, this function can be automatically managed in-line, with bottles being inspected as they’re being filled.
Safety of Workers
Robotics increase workplace safety. This is because your workers will move from performing dangerous tasks to supervisory roles where barriers are used to keep operators out of harm’s way. Robotic automation has been designed to mimic human movements. Robots eliminate difficult manual task that can lead to employees’ injuries and other ailments such as muscles strains. Robots will be used to replace humans in dangerous or injury prone condition. It can perform tasks in a critical environment that is not fit for a human, like freezing temperature or absence of oxygen. Ensuring the safety of workers is a major benefit of warehouse robotics especially in the food and beverage industry.

Time and Cost Reduction
Time and cost reductions are always at the top of the owners or Operation Manager’s mind. Robotic Process Automation is elimination difficult task like loading and unloading. Robots take the place of a human for it can carry heavy loads much more than human with accuracy; without getting tired. It can be used thousand hours at high speed before experiencing a mechanical failure and before requiring minimal maintenance. Decreasing costs is another huge benefit of warehouse automation. Although the upfront cost of adopting and implementing automation systems is anything but cheap, it pays for itself in the long run. Using automation technology becomes much cheaper than paying for manual labour in the long run.
Savings on Energy Costs and More Sustainable
Warehouses lighting will be replaced by more economical lighting source such as Light Emitting Diode (LED) and Induction Lamps. LED industrial lighting consumes only a fraction of electricity compared to the lighting source. Automated machinery and robots need no ambient lighting to operate, unlike human workers which needed bright high wattage bulbs and fluorescent lamps to work productively and safely. Also, the cost for the cooling system such as air-conditioned and industrial fans will be minimized, because robots can adapt to whatever environment they are needed. Warehouse automation can also help make warehouses more environmentally friendly, by reducing their physical footprint, waste and energy consumption. For example, smooth pallet handling ensures damage to products is minimized, the need for bright warehouse lighting is minimized, and a WMS can optimize workflows to reduce energy use.
Order Processing and Payments
When a customer selects a product and orders it through any online channel, they receive the order, shipping details, and updates electronically. But behind the scenes, many warehouse companies still depend on manual labour and paper or excel documents to execute these transactions and maintain records. This also includes manually entering the customer’s information on the company database. Automating back-office tasks through RPA BoTs, can reduce manual human work and increase efficiency. BoTs can also update regarding shipment delays or if the order needs to be canceled due to any reason. So, they can handle all aspects of order processing.

Maximizing Space
Space is a finite resource, especially in warehousing and distribution facilities that are packed with all kinds of goods. They create an ongoing game of Tetris that becomes more difficult the more you grow. Automation helps maximize the space that they have. How does it do so? For one thing, most warehouse automation systems feature robots or other machines that handle product retrieval and storage.
This means that you don’t need to send people off into the aisles which, in turn, eliminate the need for wide aisles that can accommodate bulky pallets and pallet jacks with a wide turning radius. Instead, automated warehouses feature special movable shelves that robots can move around, like goods on a pallet. However, they take up less space than a pallet, and the robots need less room to maneuver when moving them. All of this means that you can install your product shelves with smaller aisles, which creates more room for storage. In addition, automated warehouses utilize more vertical storage space. Retrieval robots and other machines can retrieve goods from high up safer and faster than humans can.
Conclusion
Implementation of RPA in warehouse automation would see changes in technology requirement and upgradation in many systems and processes. The key aspects are clarity of objective and understanding the benefits which is expected from an RPA implementation. Robotic Process Automation has also begun to show benefits towards our corporate objectives. Staying on top of these and other industry advancements is important for the future of warehouse equipment. Many of these advancements in technology and robotics could materialize savings in other parts of the business that easily justify the cost of upgrading. The best part is that they will do repetitive tasks and even involve in the risky process of human life. No need to change any of underlying business systems or applications. Scale on demand and increase business agility and no need to change any part of the existing business processes.
References
Ashwini Reddy. (2018). “RPA in Warehouse Management.” Retrieved from https://www.nalashaa.com/blog/, accessed 03/03/2019.
Culver Site Development. (2017). “Warehouse Robotic Systems – Background, Types, and Benefits.” Retrieved from https://www.culvereq.com/warehouse-robotic-systems-types-benefits/, accessed 07/03/2019.
David Roberge. (2019). “Warehouse Robotics: Are Robots the Future of Food Applications?” Retrieved from https://www.industrialpackaging.com/blog/warehouse-robotics-are-robots-the-future-of-food-applications, accessed 04/03/2019.
Ee Soon Sern, DLSM. (2018). “Autonomous Mobile Robotics for Effective Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/autonomous-mobile-robotics-effective-warehousing/, accessed 09/03/2019.
Helmi Salleh, ADLSM. (2019). “Autonomous Devices for Digital Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/autonomous-devices-digital-warehousing/, accessed 09/03/2019.
Michael Baxter. (2018). “Robotic Process Automation and Digital Process Automation: Friend or Foe?” Retrieved from http://www.information-age.com/robotic-process-automation-and-digital-process-automation-123476645/, accessed 04/03/2019.
Natasha Raymond. (2017). “Using Automation in Warehouse Logistics.” Retrieved from https://www.rtinsights.com/warehouse-automation-in-logistics-considerations/, accessed 03/03/2019
Rob O’Byrne. (2017). “The Past, Present, and Future of Technology in the Warehouse.” Retrieved from http://www.logisticsbureau.com/the-past-present-and-future-of-technology-in-the-warehouse/, accessed 03/03/2019.
Surendran, DLSM. (2018). “Adopting New Technology for Effective Warehousing.” Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/adopting-new-technologies-effective-warehousing/, accessed 10/03/2019.

