A good effective warehouse operation can significantly enhance the growth and expansion of an organization and the supply chain. Conversely, a warehouse with a poor design layout can have a negative impact on the entire operation. In order to optimize a warehouse, suitable storage equipment should be selected, both in terms of the type of system and handling equipment. The first and most important warehouse process is the receiving operation. Another aspect of the receiving operations is to transfer goods to the warehouse is. The supply chain can be optimized with an efficient run of the warehouse from inbound to outbound logistics. This article discusses several factors that are crucial for warehouse operations.

Table of Contents
Qualified Warehouse Layout
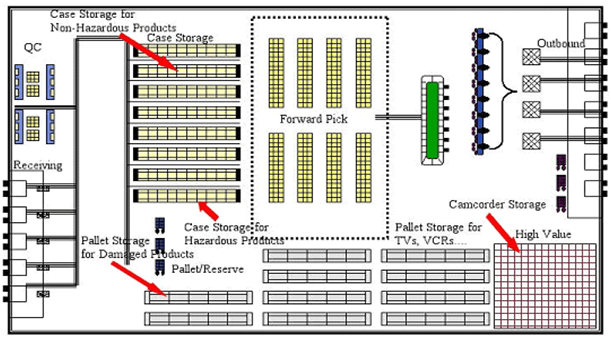
A good warehouse layout is planning to smooth the functioning of operation therefore workers can streamline the process workflow and help faster shipping. However, a poor designated warehouse layout will have a negative impact on the entire operation and supply chain. This will lead to inadequate storage space and inefficient use of the available storage. Based on the problem mentioned, the worker requires longer processing time and to manage more material due to the backtracking of the material. This will slow down warehouse operations. It would reduce the warehouse operations’ overall productivity and fulfillment rate. Before deciding on the layout for a warehouse, the objectives should clearly define what the organization needs, and what the organization wants to do and achieve at the end of the process. The layout design should clearly specify areas such as loading and unloading, picking area, packing area, sorting, storage area, reception, and dispatch area. To optimize an effective warehouse, it ensured to choose suitable storage equipment, both in terms of the type of system and handling equipment. Mostly, the handling equipment would be a pallet jack, forklift, reach truck, and self-lifting stacker. The various storage types have their own specific features that make them ideal in different situations. A good warehouse management system is crucial for solving the objectives set out in this section.
Warehouse Management System
A warehouse management system (WMS) is a software solution that helps a company manage supply chain fulfillment operations from the distribution center to the store shelf. WMS offers visibility into business’s entire inventory; it is easier to control daily warehouse operations and is likely to trace goods and materials. Nowadays, in the market, there are three main types of WMS software: standalone, cloud-based, and applications built into the enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. Each type of WMS has its own advantages and shortcoming, and the best type will be different from business to business. A standalone WMS is the most basic system among the three of them. Obviously visible the benefit of stand is often the lowest in price from the market, it is suitable for the buyer who has a lower budget. Conversely, standalone WMS is used only for its warehouse management features and tends to lack a lot of the benefits of a merged WMS solution. They are a typical on-premises type system that is used with the business’s original hardware and network. The two most key features are inventory management and warehouse operations. Cloud-based WMS’s main characteristics are hosted and managed by the vendor or a cloud service provider. They are easier to install and inexpensive to manage. Most cloud-based WMS tends to be favored by small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Larger enterprises often allocate on-premises WMS because they need extremely customized systems that meet the requirements of their specific industry, and they have the references to manage the IT requirements. An ERP system manages business information, integrates various disparate systems, streamlines workflows, and achieves efficiency. An efficient ERP solution coordination and merge three key flows: material flows, information flows, and financial flows. It streamlines the path their products go from supplier to warehouse and finally to the store for the customer.

Choosing the Right Technology
The current state of globalization and the development of the internet place pressure on businesses to offer more value-added services, improved service standards, cost-effectiveness, and transaction traceability. The business will not be able to compete in the market or with its rivals if it does not upgrade the warehouse service using technology. By using WMS, a warehouse may optimize order picking, order shipping, and inventory replenishment while reducing human error and performing paperless inventory receiving and put-away. The organization and distribution sector has traditionally used handheld technologies like barcode scanners, but recent developments have made them more effective and practical than ever. To improve efficiency and lower theft and inventory loss, warehouses that still use manual counts and paper paperwork should think about switching to digital inventories and mobile devices with RFID scanners and GPS. Although it is a time-honoured custom to pack and label products by hand, doing so increases the risk of packing and shipping mistakes. Print-and-apply labeling systems eliminate the chance of human error by automatically labeling and closing packages in accordance with their contents. These technologies can function independently when coupled with IoT systems, avoiding expensive shipping errors.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.

