Tropical fruits originate from regions with tropical climate environment. But tropical fruit does not mean that the fruit is limited to the region, as some farmers from warm temperate regions may grow them, just like subtropical fruits are occasionally grown in tropical regions. Tropical fruits are very sensitive to the temperature of cold and frost. Varies in different shapes, sizes, and flavors, bright colors, and fragrances, which are the reasons for attracting other factors.
Tropical fruits are important to businesses in many developing countries. It aims to attract business in the highly competitive tropical regions and create job opportunities to increase foreign income and develop a global supply market for them. Tropical fruits are very delicious with tangy and sweet flavours and usually have high level of water content. It benefits to the human health, including minerals, vitamins, fiber, antioxidants, and carbohydrates in some cases, that nourishes the body. Tropical fruits are also beneficial to the digestive tract, skin, and hair.
Table of Contents
Sourcing Tropical Fruits
The fruit production harvest and export in the tropical regions include:
- Asian region
The Asian countries include Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, and the Philippines. They mainly produce and export bananas, pineapples, and mangoes, watermelons, pineapples, bananas, papaya, and mangoes.
2. African region
The African countries include South Africa, which mainly produces and exports tropical fruits including oranges, tangerines, grapes, dragon fruits, pomegranates, and stone fruits.
3. Latin America and the Caribbean region
The Latin American and Caribbean countries include the Bahamas and Mexico, Ecuador, Argentina, and Chile. They mainly produce and export tropical fruits including banana, mango, pineapple, avocado, and papaya
The Seasonal Factor
In tropical fruit countries, temperatures are hot and humid throughout the year, with occasional monsoon raining months. However, the fruit passes through two different production seasons, including:
- Non-seasonal
It is easy to find tropical fruits that can be harvested throughout the year. Examples of non-seasonal tropical fruits include guava, papaya, pineapple, banana, jackfruit.
2. Seasonal
Seasonal fruits only produce fruits at certain times, harvesting according to season and month. Tropical fruits usually decline from June to August, while the off-season is from December to February. This kind of fruit has limited production. Some may only produce once a year and according to the season. Some famous seasonal tropical fruits include Durian, Mangosteen, Orangutan, Duke, Langsat and Mango.
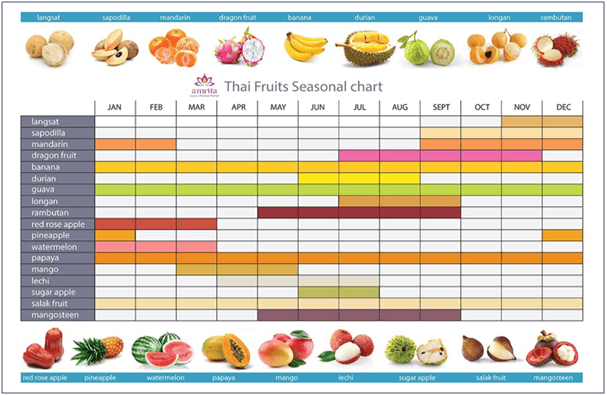
The Price Factor
The price of tropical fruits fluctuates between the months of the year. The price changes seasonally. When the fruit season begins, the amount of fruit harvested is relatively small. Market prices will rise and become more expensive. When the production season peaks, the harvested yield leads to oversupply. on this time, the price of fruit drops and it will be cheaper. Purchaser therefore buys in large quantities for storage and supply market demand when in non-seasonal months. Lack of control in quality storage and fruit life calculation will lead to losses, just like durian, where the production is usually relatively small and the price is expensive. The prices will drop from July to September due to peak harvesting.
There are two styles of tropical fruits to purchase and sell. They include weight and grain size trading. First, fruits are classified into size. Merchants divide fruits into 2A, 4A, and 6A. There is no strict definition for this level. 2A refers to small fruits, 4A Refers to the medium size fruits, and 6A refers to the large size fruit. The cost of large-sized fruits will be higher, and they will almost be bought and sold in single unit. The cost of the small size will be cheaper, which will be package to grams and kilograms, where most of the traded is by weight. Purchasing tropical fruits will using these two methods to define the price

The Quality Factor
The collection of some tropical fruits has become more valuable. When the tropical fruit season is over, the market will cause a shortage of fruit products and supply shortages, and the inventory on hand will become very valuable. Buyers will buy a lot of storage space before the end of the season, because tropical fruit products will be very cheap at this time, but the risk will be heightened as these fruits are easy in deteriorating and rotten. During the collection period, quality inspection and temperature control are essential to reduce risk. If the quality of the fruit is not controlled, losses and wastage will be unavoidable.
The Supply Availability Factor
Tropical fruits are picked before the tree matures, due to many factors, including harvesting methods, packaging, storing and transportation to the market. Tropical fruit are climacteric fruit, highly perishable, calculating the fruit quality and time is of great essence. The fruit ripes easily, hence the grower needs to harvest the fruit in a controlled size when it is still unripen, for the long-distance transportation without loss of quality, and some growers will use ethylene in accelerating the ripening of the fruit

The Factor of Inventory and Storage
Fruits accumulate a lot of water during the long-term maturity period, and also lose a lot of water during the mature period. All tropical fruits should be stored in low temperature to prevent further deterioration. Most tropical fruit are sensitive to low-temperature storage, and temperature storage and transportation are controlled between 13 ±1°C.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
A Systems Approach. (2014). “Postharvest Physiology and Quality Maintenance of Tropical Fruits Author links open overlay panel”. Retrieved from https: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780124081376000107, accessed 06/12/2020.
Ahmad A, etc. al. (2013). “Delayed Softening of Papaya”. Retrieved from https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11356-016-8197-5, accessed 06/12/2020.
Evelyn Seow Pick Ling, DPSM. (2020). “Global Sourcing Consideration for Food Retail Distribution”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/global-sourcing-considerations-food-retail-distribution/, accessed 06/12/2020.
Rozhan Abu Dardak. (2019). “Trend in Production , Trade, and Consumption of Tropical Fruit in Malaysia”. Retrieved from https://ap.fftc.org.tw/article/1381, accessed 06/12/2020.
Yvonne Ong Hwee Ping, DPSM. (2020). “Lean Procurement Practices for Reducing Food Waste”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/lean-procurement-practices-reducing-food-waste/ , accessed 06/12/2020.

