The inventory stock within the food industry is usually perishable. Thus,the manner in which a company handles and manages their food inventory is critical to the safety of the products. A successful organization will have a good inventory techniques to handle the availability chain, distribution of the goods to ensure safety of the products for consumers.
Table of Contents
First-In-First-Out (FIFO) Technique
First-in-first-out also known as FIFO method is an asset-management and inventory valuation method in the first goods purchased and first goods sold, used, or disposed off. FIFO is a useful technique, especially in the food industry for perishable food and those that have a shorter shelf life. Most retailers will be using the newest stock to fulfill orders, that leaves the older inventory sitting in the warehouse going pass their sell by date. By displaying the newer goods at the back of the shelves, this can help to clear the older goods, and thus reduce cost and prevent wastage.
ABC Analysis Technique
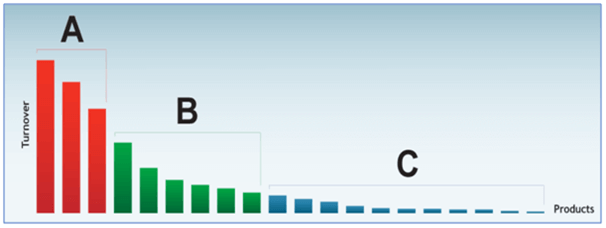
ABC analysis is used to classify stock inventory based on its values and consumption over period of time, for example, a year. The stock values and consumption in category A is the highest as compared to category B. Category C is the lowest amongst these three categories. Most companies choose to focus and concentrate on managing the stocks in category A to increase the potential in cost reduction. As the value and consumption for categories B and C are lower, companies allow buffer stocks in these categories to prevent the stock-out situation. ABC analysis of inventory is one method that uses the Pareto principle as the basis for the technique. Inventory can be categorized based on the 80-20 rule, and priorities and manage as separately and selectively. It states that 80% of sales come from 20% of the product lines and 80% of sales come from 20% of the customers.
Just-In-Time Technique
Just-in-time (JIT) is a common inventory management technique used to increase efficiency and eliminate waste. Receiving goods only when they are needed in the production process accordingly will help to reduce the unnecessary operating costs. In order words, JIT inventory refers to an inventory management system with the objectives of having inventory readily available to fulfill the need, but not to a point of excess where you store extra products.
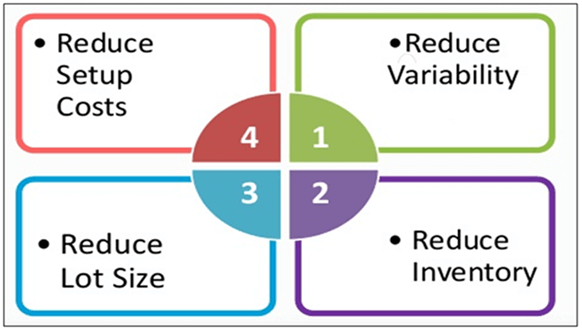
JIT inventory management tools are based on elimination of all waste and continuous improvement, also referred to as lean production and applied to repetitive manufacturing processes. JIT inventory control can help to reduce inventory levels, variability, shorter delivery time, and lower setup costs.
Batch Tracking Technique
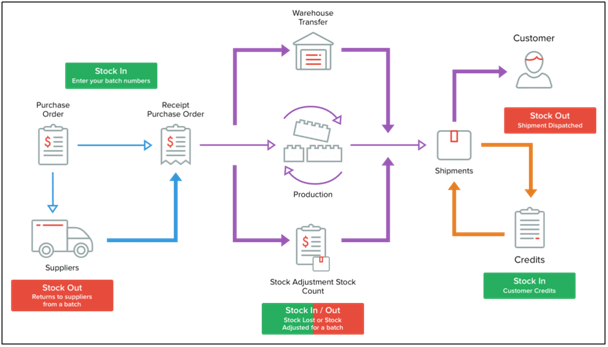
Batch tracking is one of the controls of quality inventory technique, wherein users can group and monitor a set of stock with a similar feature. This method enables tracking of the product expiry dates, analyzing the return rates for certain batches, and make accurate reports on revenue, profit margin report, and simple moving average, etc.
Backorder Management Technique
A backorder is defined as an order that cannot be fulfilled immediately due to the stock unavailability.Backorder is used to prevent stockpiling and proper managing of backorder allows the company to have a higher positive net value as it decreases the storage cost. However, improper managing will cause the customer to look for other alternatives to prevent customer dissatisfaction; forecasts are used to manage the stock lead time for backorder.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Technique
Economic order quantity, also as known as EOQ is a procedure to determine the ideal order quantity is a company should purchase to minimize inventory costs such as ordering, holding, and shortage costs. This formula can be used to determine the most effective amount of goods that order and carry cost may be reduced to a minimum point. EOQ is a level of inventory order that an avoid out of stock or overstocking and minimizes the ordering and total holding costs.
EOQ is a decision tool that is used in cost accounting. The formula is used to calculate the ideal quantity of inventory to place an order. This is designed to minimize order and carrying costs to avoid running out of inventory and fulfill all customer’s orders. EOQ assumes the timing for reordering at a specific reorder point.
The EOQ is a very simple model and its assumptions will be unpractical in many applications, in practice orders are not delivered instantly. The assumption of the constant usage of inventory and known annual demand are of suspicious justifiability.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Chua Seok Khim, DPSM. (2019).“Crucial Techniques to control Construction Inventory”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/crucial-techniques-control-construction-inventory, accessed 09/09/2020.
Lee Yi Xian, DLSM. (2019).“Inventory Control Techniques for Effective Warehousing”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/inventory-control-techniques-effective-warehousing, accessed 09/09/2020.
Marello. (2020). “Inventory Batch Tracking: Streamline your Inventory Management”. Retrieved from https://www.marello.com/2020/02/25/inventory-batch-tracking, accessed 10/09/2020.
Sung Bee Ying, DLSM. (2020). “Essential Techniques for Control of Warehouse Inventory”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/essential-techniques-control-warehouse-inventory, accessed 10/09/2020.

