While the use of various chemicals in experimental research is essential, it is also important to safely store and maintain them as a part of the Environmental, Health and Safety (EHS) program. The properties of chemicals and their reactivity vary broadly and if chemicals are not managed, stored, and labeled properly, they can have harmful or even destructive consequences such as toxic fume production, fire or explosion, which may result in a human fatality, property damage or environmental hazards.
Therefore, an appropriate chemical label should identify the material and list the associated hazards, and users should have knowledge of how to read chemical labels and safety data sheets (SDS). Proper chemical storage must meet OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Association) standards and this can prevent most chemical reactivity hazards.

Table of Contents
Identifying Substances Used
The first (and arguably the most important) step in storing hazardous chemicals safely is to identify each substance you have onsite to gain an understanding of their properties and their hazards. Is the chemical flammable, toxic or corrosive? Is it self-reactive or does is react to sunlight? Is it incompatible with other substances? Can it negatively affect the environment or aquatic life?
To find out you’ll need the Safety Data Sheets (SDS) provided by the manufacturer, importer or supplier and then study them closely. The SDS will specify the storage requirements for the chemicals and any incompatible substances or environmental conditions that might cause an adverse reaction like a fire or explosion. Chemical and physical properties define the hazards of a chemical. However, in a chemical storage facility, further factors add on: quantity, storage form.

Assessing Risks Associated with Chemicals
Once you have identified the hazardous chemicals in your workplace you should assess the risks that may arise from their storage, handling and use, as well as the extent of the risk, so that this will allow you to take appropriate risk control measures.
The first step in assessing the risks of hazardous chemicals is to read the safety data sheet (SDS). The SDS provides information about the health hazards if it is breathed in, swallowed, or if there is contact with the skin or eyes. It also provides other hazard information such as whether it is flammable or toxic.To properly understand the risks involved with certain hazardous chemicals, you should consult all health and safety resources available to you.
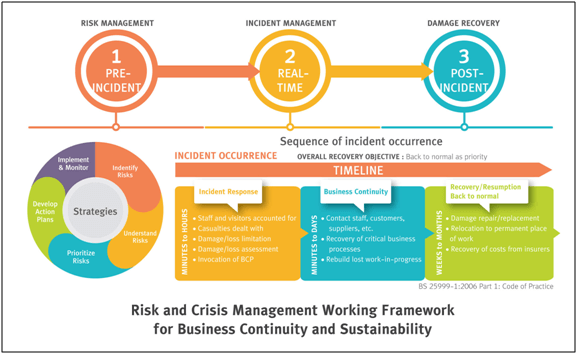
Risk and crisis management procedures for business continuity and sustainability have been embedded into regular business operations and tailored to suit all internal corporate functions. Our Risk Culture, which adopts a working framework designed for both top-down and bottom-up approaches, encourages engagement at all levels and ensures that risk management plans and measures are practical and effective.
The working framework comprises of 3 key steps: Pre-incident risk management, real-time incident management, and post-incident damage recovery, as reflected in the diagram below:
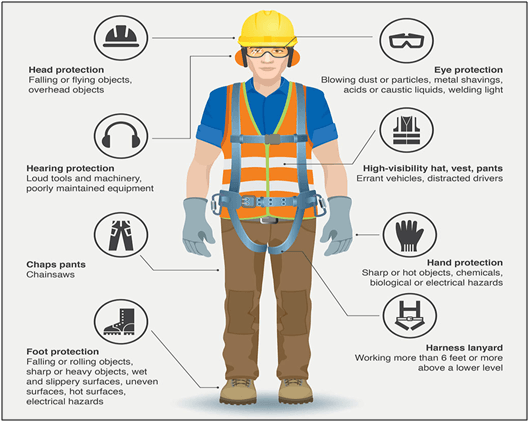
Personal Protective Equipment
Any work involving hazardous chemicals should be established and documented through written procedures. The procedures should cover dispensing, transferring, using and disposing of the hazardous chemicals. During the manufacturing process of the chemicals, written procedures should be put in place for the start-up, during routine operation, at shut down and maintenance work. The safe work procedures should include the safety and health precautions which are to be taken during the course of work, and the use of personal protective appliances.
Personal protective equipment (PPE) includes respirators, safety glasses, face shields, coveralls, aprons, gloves and boots. Fit tests should be conducted for respirators used by the workers, and the fit test certificates should be kept. Workers should also conduct fit checks (positive or negative pressure fit checks) on their respirators before using them. It is a good practice to perform leak tests on PPE such as gloves to check for holes before use. PPE should be selected properly, used correctly or comfortably fitted and maintained regularly to ensure effective protection. A suitable PPE should be implemented with taking the preceding elements (i.e., selection, issue, fitting and maintenance) into consideration.
Checklist for transporting hazardous chemicals
• Avoid transporting chemicals with food, water or other reactive chemicals
• Follow the separation and segregation rules for transporting mixed classes of Hazardous chemicals (those classified as dangerous goods)
• Secure hazardous chemicals on the vehicle so they can’t move or fall
• Keep a record of the chemicals you are carrying
• Separate foodstuffs from chemicals
• Make sure you have the required signs and equipment for the vehicle
• Make sure the driver of the vehicle has the correct license and is trained in emergency procedures.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Amran Hossain, DLSM. (2019).”Key considerations for Warehousing Safety and Health“. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/key-considerations-warehouse-safety-health, accessed 17/12/2019.
David Chew, DLSM. (2019).”Four Key Areas for Mitigating Warehouse Risks“. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/four-key-areas-mitigating-warehouse-risks, accessed 17/12/2019.
Jove Cambridge MA, (2019).”Chemical Storage: Categories, Hazards, and Compatibilities”. Retrieved from
https://www.jove.com/science-education/10380/chemical-storage-categories-hazards-and-compatibilities,accessed 17/12/2019.
Queensland Government. (2019).”Risk Management”. Retrieved from https://www.business.qld.gov.au/running-business/protecting-business/risk-management/hazardous-chemicals/assess-risks,accessed 17/12/2019.
Vince Mcleod. (2017).” Handling and Storing Chemicals”. Retrieved from https://www.labmanager.com/lab-health-and-safety/2017/07/handling-and-storing-chemicals#.XfpN9W5uI2x,accessed 17/12/2019.
Walter Ingles (2018).”5 steps to Storing Chemicals Safety in the Workplace”. Retrieved from https://blog.storemasta.com.au/5-steps-storing-chemicals-safety-workplace, accessed 17/12/2019.

