According to 2020 Report to the Nations, The Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE) estimated that the organisations lose up to 5% of revenue to fraud every year and corruption was the most common practice in every country. Reasons for employee in committing procurement fraud include perceived financial pressure, perceived opportunities and rationalization. Procurement fraud does not only result in financial loss but also tarnish the reputation of an organisation. It is crucial for the management to take action in combating procurement fraud before it imposes greater damage to the organisation. This article discusses the key factors to prevent frauds in the procurement function of an organisation.
Table of Contents
Segregation of Duties
A key strategy of risk management and internal control is to separate duties. Empowering one person with complete control of a business process or an asset can pose greater risk to an organisation. To make the internal control effective, an adequate division of responsibilities among the individuals or departments who place orders, handle assets and those who authorise payment or accounting procedures should be in place.
This concept is to promote shared responsibilities of a critical process, and that no employee should perform more than two of the following functions:
- The custody of assets
- Authorisation or approval
- Recording or reporting
For instance, the person who issues purchase order should be different from the person who will be approving the purchase order. The person who authorises the payment should not be the person who approves the purchase of goods or services.
Regular Compliance Audits
Internal audit acts as a firewall to reduce the financial and reputational impact of fraud but also in preventing detriment to business objectives. Audits should be systematically planned in order to ensure all the procurement processes were carried out ethically and compliance with purchasing policies and procedures. This will be very helpful to ensure the organisation conforms to best practices and improves the operational efficiency.
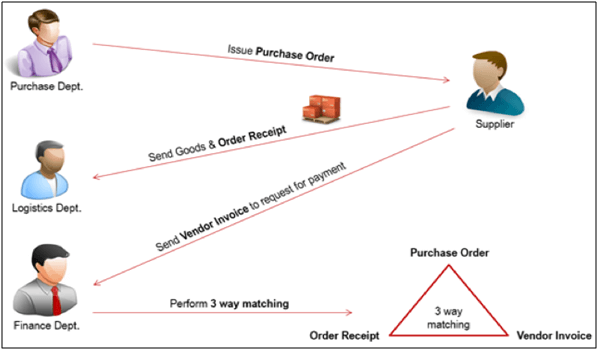
Implementing a positive internal control environment helps to ensure the organisation conforms to best practices and improves the efficiency in operation. A robust internal control system should include:
- Separation of duties
- Physical safeguards over assets
- Proper documentation
- Proper authorisations
- Adequate supervision
- Independent validation of transaction
Precautionary measures that can be implemented to improve compliance include conducting sample audits to check veracity of invoices, and whether goods and services have been delivered as documented on the receiving report. Aside, the quality of goods and services should be monitored regularly to ensure they are meeting the requirements and all the invoices should match with the prices in the contract. 3-way match should be implemented for each invoice to secure matching between order, receiving and supplier’s invoice.
Supplier Pre-Qualification
Procurement process usually begins with the selection of a supplier. Hence, it is essential to check on the financial stability, reputation, record tracking, conflict of interest and business culture of suppliers prior to engaging in any business activities. In addition, supplier due diligence should be performed during every supplier approval process. They should be thoroughly checked and verified by at least two persons. Approved vendors list that maintained by the procurement organisation will include those suppliers that are successful in meeting the pre-qualification criteria. It is an effective method of gaining knowledge of specific group of suppliers with the primary aim of minimising cost and risk for both parties- buyers and suppliers.
Clear Purchasing Policy and Ethical Conduct
Establishing and maintaining an ethical environment as well as a culture of honesty within the organisation are very important in preventing fraud. Clear and well-written purchasing policies and procedures are utmost important to allow employees to understand their roles and responsibilities within predefined limit. Additionally, it also demonstrates the organisation’s commitment in ensuring all procurement activities are conducted in an honest, competitive, fair and transparent manner. The policies and procedures should receive regular reviews and improvements to remain relevant.
The duties of procurement professional include avoid conflicts of interest and personal enrichment, treat suppliers equally and fairly, conduct duties with care and diligence and compliance with legal and other obligations. Everyone should uphold the integrity in execute all the procurement activities and be accountable for abiding all the ethical standards of an organisation.
Clear Criteria for Sourcing and Supplier Selection
All evaluation criteria should be presented prior to sourcing and tender submissions to maintain fairness and transparency in the procurement process. Collaborating with stakeholders to determine goal and priorities is essential in defining clear supplier selection criteria. An organisation should create a list of important factors and this list should serve as a guideline in selecting winning supplier. A transparent guideline in supplier selection will help to prevent any procurement professional in abusing his or her right in rewarding a particular supplier.
The full content is only visible to SIPMM members
Already a member? Please Login to continue reading.
References
Association of Certified Fraud Examiners, (2020). “Report To the Nations”. Retrieved from https://acfepublic.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/2020-Report-to-the-Nations.pdf, accessed 10/09/2021.
Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, (2014). “Preventing Procurement Fraud and Corruption”. Retrieved from https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/za/Documents/risk/ZA_RA_PreventingProcurementFraudCorruption_2015.pdf, accessed 12/09/2021.
Doreen Chow Fong Meng, DPSM. (2019). “Crucial Strategies to Prevent Procurement Fraud”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/crucial-strategies-prevent-procurement-fraud/, accessed 09/09/2021.
Emma Zhang, (2016). “Segregation of Incompatible Duties”. Retrieved from https://www.carrtegra.com/2016/05/segregation-incompatible-duties/, accessed 13/09/2021.
Ivy Ng Lian Leck, DPSM. (2018). “Six Key Strategies to Avoid Procurement Fraud”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/six-key-strategies-avoid-procurement-fraud/, accessed 09/09/2021.
Liong Sze Pei, DPSM. (2020). “Fraud Prevention Strategies for Construction Procurement”. Retrieved from SIPMM: https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/fraud-prevention-strategies-construction-procurement/, accessed 09/09/2021.
National Association of State Procurement Officials, (2019). “Importance of Ethical Procurement”. Retrieved from https://www.naspo.org/Toolbox%20Issue%202.pdf, accessed 12/09/2021.
Tufts University,(2021). “Fraud Prevention”. Retrieved from https://sites.tufts.edu/amas/controls-compliance/fraud-prevention/, accessed 13/09/2021.

